Researchers discover master regulator in cancer metastasis
In the process of metastasis, the movement of cancer cells to different parts of the body, a specific master regulator gene plays a central role: a transcription factor named Sox4 activates a sequence of genes and triggers the formidable process. This finding is reported by researchers from the University of Basel and from the Friedrich Miescher Institute in Cancer Cell. Inhibition of Sox4 and subsequent processes may prevent metastasis in cancer patients.
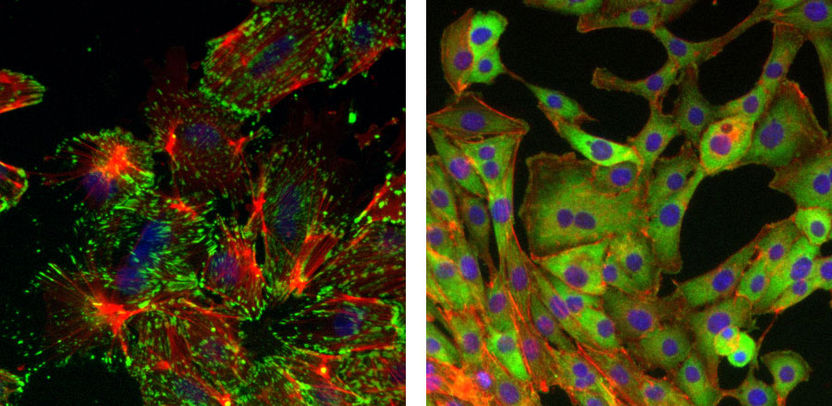
Mammary epithelial cells that have undergone an epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (left image), exhibit a change in cell morphology with actin stress fibers (red) and with focused cell adhesion points (green). In mammary epithelial cells in which the Sox4 transcription factor is missing (right image), this change is not apparent, and cancer cells cannot metastasize.
Dr. Nathalie Meyer-Schaller, Universität Basel
The predominant cause of death in cancer patients is metastasis, the formation of secondary tumors in other organs like the brain, liver, and lungs. Cancer cells detach from the original primary tumor and reach a single cell or group of cells in another organ. The cells of the body normally remain in place through adhering to an extracellular substance. However, cancer cells learn how to release themselves from these bonds and invade surrounding tissues, blood, and the lymphatic system.
The transformation of sedentary, specialized cells into wandering, invasive, and unspecialized cells is called epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which is central to metastasis. EMT is a multistage process, which is accompanied by a fundamental change in cell morphology and number of genetic programs. The molecular processes that govern EMT, however, are still poorly understood.
Main switch found
The research groups of Prof. Gerhard Christofori of the Department of Biomedicine at the University of Basel; Prof. Erik van Nimwegen from the Biozentrum, University of Basel; and Prof. Dirk Schuebeler from the Friedrich Miescher Institute have discovered a master regulator of EMT and metastasis: the transcription factor Sox4 is upregulated in its activity and triggers the expression of a number of genes that play an important role during EMT and metastasis.
In particular, Sox4 promotes the expression of the enzyme Ezh2, a methyltransferase, which generally influences methylation of specific proteins (histones), the packaging of the genetic material, and thus its readability and gene expression. Due to this change in genetic information, the behavior and function of cells are reprogrammed - a process that is currently observed during metastasis. Such a change in gene expression is also found in patients with malignant cancer and metastasis and correlates with a poor prognosis.
These findings point to the possibility that the inhibition of the transcription factor Sox4 and especially the methyltransferase Ezh2 could hinder metastasis in cancer patients. Appropriate medications are currently being developed but they need to undergo clinical trials before being used in patients. The research was implemented within the framework of the SystemsX.ch-RTD Project „Cell Plasticity.”
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.