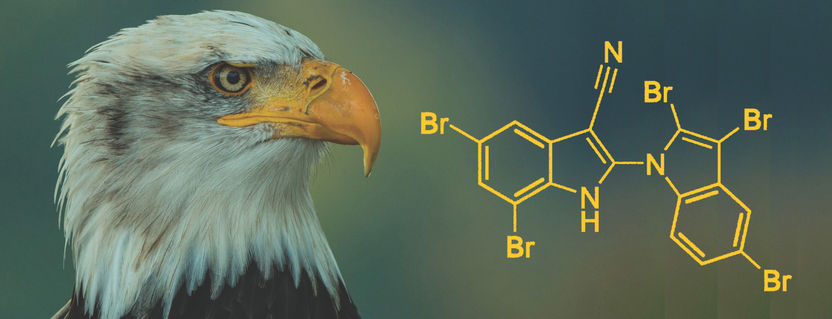
New gene variant may explain psychotic features in bipolar disorder
Advertisement
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have found an explanation for why the level of kynurenic acid (KYNA) is higher in the brains of people with schizophrenia or bipolar disease with psychosis. The study identifies a gene variant associated with an increased production of KYNA. The discovery contributes to the further understanding of the link between inflammation and psychosis – and might pave the way for improved therapies.
Kynurenic acid (KYNA) is a substance that affects several signalling pathways in the brain and that is integral to cognitive function. Earlier studies of cerebrospinal fluid have shown that levels of KYNA are elevated in the brains of patients with schizophrenia or bipolar diseases with psychotic features. The reason for this has, however, not been fully understood.
KMO is an enzyme involved in the production of KYNA, and the Karolinska Institutet team has now shown that some individuals have a particular genetic variant of KMO that affects its quantity, resulting in higher levels of KYNA. The study also shows that patients with bipolar disease who carry this gene variant had almost twice the chance of developing psychotic episodes.
KYNA is produced in inflammation, such as when the body is exposed to stress and infection. It is also known that stress and infection may trigger psychotic episodes. The present study provides a likely description of this process, which is more likely to occur in those individuals with the gene variant related to higher production of KYNA. The researchers also believe that the discovery can help explain certain features of schizophrenia or development of other psychotic conditions.
"Psychosis related to bipolar disease has a very high degree of heredity, up to 80 per cent, but we don't know which genes and which mechanisms are involved," says Martin Schalling, Professor of medical genetics at Karolinska Institutet's Department of Molecular Medicine and Surgery, also affiliated to the Center for Molecular Medicine (CMM). "This is where our study comes in, with a new explanation that can be linked to signal systems activated by inflammation. This has consequences for diagnostics, and paves the way for new therapies, since there is a large arsenal of already approved drugs that modulate inflammation."
Original publication
Catharina Lavebratt, Sara Olsson, Lena Backlund, Louise Frisén, Carl Sellgren, Lutz Priebe, Martin Schalling et al., 'The KMO allele encoding Arg452 is associated with psychotic features in bipolar disorder type 1, and with increased CSF KYNA level and KMO expression', Molecular Psychiatry, 2013.