Towards a new moth perfume
A single mutation in a moth gene has been shown to be able to produce an entirely new scent. This has been shown in a new study led by researchers from Lund University in Sweden. In the long run, the researchers say that the results could contribute to tailored production of pheromones for pest control.
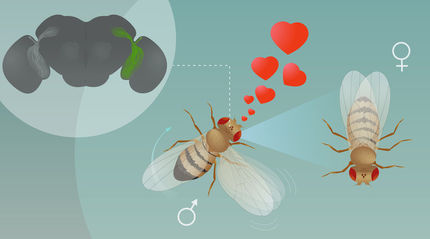
Male moths can pick up the scent of a female moth from a distance of several hundred metres. The females produce sexual pheromones – scent substances that guide the males to them. There are around 180 000 species of moth and butterfly in the world, and most of them communicate using pheromones. Small differences between the different scents enable the males to find females of their own species.
Researchers at Lund University have previously shown that new species of moth can evolve as a result of changes in the female moths’ scent. Now the researchers have published a study on how these changes come about at genetic level.
“Our results show that a single mutation, which leads to the substitution of a critical amino acid, is sufficient to create a new pheromone blend”, says Professor Christer Löfstedt from the Department of Biology at Lund University.
The study has been carried out together with researchers in Japan and focuses on a moth genus called Ostrinia. The researchers have studied one of the genes that control the production of pheromones. It is in this context that the mutation and the substituted amino acid in an enzyme have shown to result in a new scent substance. The enzyme is active in the process that converts fatty acids into alcohols, which constitute the ingredients in many moth scents.
“Pheromones are already one of the most frequently used methods for environmentally friendly pest control”, says Christer Löfstedt. “With this knowledge, we hope in the future to be able to tailor the production of pheromones in yeast cells and plants to develop a cheap and environmentally friendly production process.”
Most read news
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.