The neurobiological consequence of predating or grazing
Scientists from Tuebingen compare neuronal network connections in two worm species
Researchers in the group of Ralf Sommer at the Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology in Tuebingen, Germany, have for the first time been able to identify neuronal correlates of behaviour by comparing maps of synaptic connectivity, or “connectomes”, between two species with different behaviour. They compared the pharyngeal nervous systems of two nematodes, the bacterial feeding Caenorhabditis elegans and the predator/omnivore Pristionchus pacificus and found large differences in how the neurons are “wired” together.
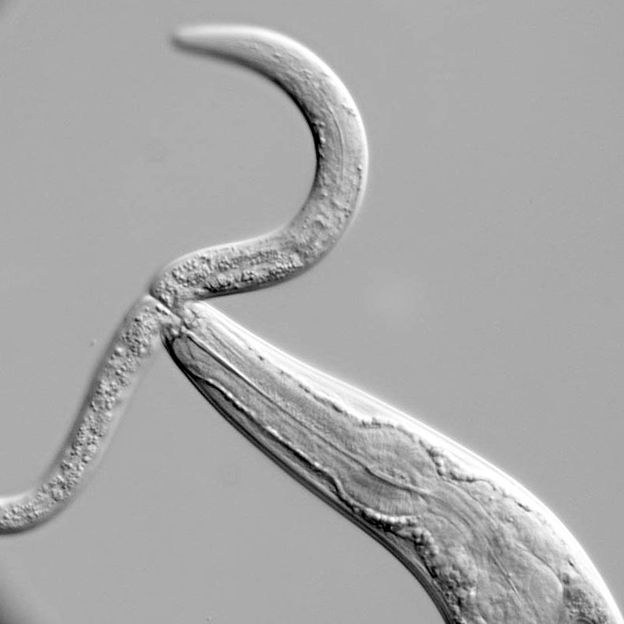
Pristionchus can prey on other worms if bacteria get scarce. Here C. elegans is the prey.
© MPI for Developmental Biology
A long standing question in neurobiology is how certain behaviours are reflected in the pattern of connections between neurons. Answering this question requires a comparative approach, which has proved impossible even in a rather small organism like the nematode due to technical limitations in the preparation and analysis of the extremely large data sets. Dan Bumbarger and his colleagues have chosen the pharyngeal nervous systems of C. elegans and P. pacificus, which consist of only 20 neurons and show a high degree of independence from the body nervous system. These 20 neurons regulate the contraction of the pharynx muscles which are responsible for the uptake of food and its processing prior to digestion in the intestine.
Bumbarger has prepared ultra-thin sections of two Pristionchus worms and compared the number and location of synapses in the pharynx nervous system with the existing C. elegans data. Despite the small size of a nematode, data generation and analysis took over three years: Each of the 150 micrometre long pharynx regions yielded more than 3000 sections that had to be individually imaged and analysed under the electron microscope.
The first result of this extensive study came as a surprise: “By means of their shape and position each of the 20 neurons in Pristionchus pacificus could be correlated to an exact equivalent in Caenorhabditis elegans” explains the scientist. “This is all the more astonishing as the evolutionary distance between the two worm species is over 200 million years and they differ markedly in feeding behaviour and in the anatomy of their mouth parts.” While C. elegans feeds exclusively on bacteria, P. pacificus is able to switch its behaviour to prey on other worms if bacterial food gets scarce.
These differences are reflected in the number and position of neuronal synapses. While in C. elegans only 9 out of 20 nerve cells are motor neurons, which primarily activate muscle cells, the number is up to 19 in P. pacificus; only one neuron functions exclusively as an interneuron, establishing connections between nerve cells. “This hints at substantial differences in information flow”, states Ralf Sommer. Clearly, the regulation of movements is much more complex in P. pacificus – a finding which correlates perfectly with the predatory feeding behaviour of the worm.
By means of partly newly developed analytical methods the scientists in Tuebingen also compared the relevance of individual neurons and synapses for the entire network. It became obvious that two neurons in the anterior part of the P. pacificus pharynx have significantly gained in importance: They are the motor neurons regulating the muscle cells that control the movement of mouth parts, most prominently the movement of teeth which are not found in C. elegans. “The mouth parts are particularly active during a predatory attack, but not when feeding on bacteria” explains Sommer. In C. elegans, these two neurons function exclusively as interneurons. There are marked differences in the posterior part of the pharynx as well. This is where C. elegans has a specialized muscular “grinder” for crushing bacteria, their only food source. In P. Pacificus, which does not have a grinder, some of the muscle cells have lost synaptic connections with neurons.
“The patterns of synaptic connections perfectly mirror the fundamental differences in the feeding behaviours of P. pacificus and C. elegans”, Ralf Sommer concludes. A clear-cut result like that was not what he had necessarily expected. Previous studies in much simpler neural circuits - as in the marine snail Aplysia – had indicated that changes in behaviour do not have to coincide with changes in number and location of synapses. Differences in physiological properties of neurons or in their modulation by neurotransmitters can be sufficient to effect behavioural changes.