Multiple sclerosis: New marker could improve diagnosis
Researchers identify potassium channel as an autoantibody target
Advertisement
Diagnosing multiple sclerosis (MS) is a challenge even for experienced neurologists. This autoimmune disease has many symptoms and rarely presents a uniform clinical picture. New scientific findings on the immune response involved in MS could now help improve the diagnosis of this illness. Scientists analyzing the blood of MS patients have discovered antibodies that attack a specific potassium channel in the cell membrane. Potassium channels play an important role in transmitting impulses to muscle and nerve cells and it is exactly these processes that are inhibited in MS patients.
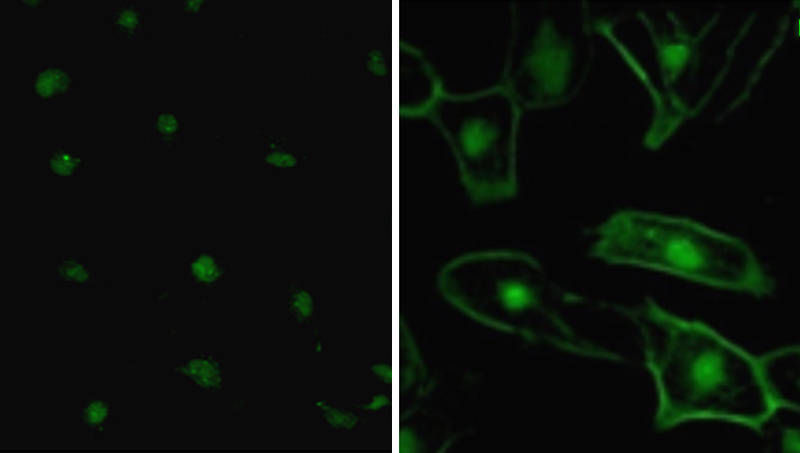
Right: The autoantibody can be seen binding to the membrane of glial cells in the MS serum. By comparison, the image on the left shows a blood sample from a patient with another neurological.
KKNMS
For the first time, scientists in Germany’s multiple sclerosis competence network have been able to identify an antibody that bonds with the potassium channel KIR4.1. “We found this autoantibody in almost half of the MS patients in our study,” explains Bernhard Hemmer, Professor of Neurology at the Klinikum rechts der Isar hospital at Technische Universität München (TUM). The biomarker was not present in healthy patients. The findings could therefore indicate that KIR4.1 is one of the targets of the autoimmune response in MS. Humans and animals without the KIR4.1 channel experience neurological failure and cannot coordinate their movements properly. Furthermore, their bodies do not create sufficient amounts of myelin, a layer of insulation that protects the nerve cells.
KIR4.1 is primarily present in the membrane of glial cells, which are responsible for controlling metabolism in the brain and forming myelin. The neurologists will now be conducting follow-up studies into how KIR4.1 antibodies influence the development of MS. This autoantibody is extremely rare in people with other neurological diseases, making it an important potential diagnostic marker for MS in the future. “This autoantibody could improve diagnosis of MS and help us differentiate it more clearly from other neurological diseases,” continues Hemmer. This will also be the focus of further research.
The study was funded by Germany’s Federal Ministry of Education and Research within the framework of the competence network for multiple sclerosis (CONTROLMS research association).