Direct transfer of plant genes from chloroplasts into the cell nucleus
Gene function preserved despite structural differences in the DNA
Advertisement
Chloroplasts, the plant cell’s green solar power generators, were once living beings in their own right. This changed about one billion years ago, when they were swallowed up but not digested by larger cells. Since then, they have lost much of their autonomy. As time went on, most of their genetic information found its way into the cell nucleus; today, chloroplasts would no longer be able to live outside their host cell. Scientists in Ralph Bock’s team at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology have discovered that chloroplast genes take a direct route to the cell nucleus, where they can be correctly read in spite of their architectural differences.
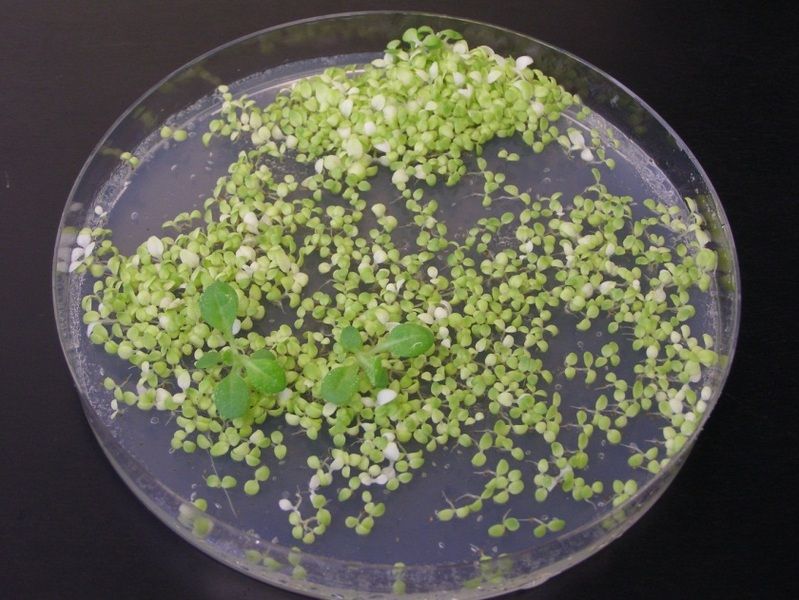

Fast-forwarding evolution. A gene’s jump from the chloroplast genome into that of the nucleus is made visible here through the development of antibiotic resistance. In the two green shoots, the resistance gene has migrated into the cell nucleus, where it can be correctly read, thus allowing the plant to grow on an antibiotic-containing medium.
© Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology
Cyanobacteria are among the oldest life forms, and appear to be the forerunners of green chloroplasts in plant cells. They do not possess a true cell nucleus, but their genetic substance is made up of the same four building blocks as that of humans, plants and animals. Therefore, the genes encoded in the chloroplast DNA can also be read in the cell nucleus; indeed, many genes that were still found in the cell organelles during early evolution are now located exclusively in the genome of the nucleus. How they made their way there has previously been unclear. Two mechanisms appeared likely: either direct transport in the form of DNA fragments from the chloroplasts to the nucleus or transport in the form of mRNA, which is then transcribed back into DNA.
The direct transfer of DNA appears to predominate in the chloroplasts, but this pathway raises two problems. The first problem lies in the promoters, the DNA sequences which ensure that genes are recognised as such. They are located upstream of the genes and recruit proteins that are required for transcription of the genes. However, promoters from chloroplasts are not recognised as such by the proteins in the nucleus, so that the DNA reading machinery should overlook these incoming genes.
The second difficulty is in the correct processing of the gene sequence. Genes consist of several modules, separated by non-coding DNA regions (introns). Since the introns obstruct protein synthesis, they need to be removed from the mRNA, a procedure described as splicing. The whole process, ending in synthesis of the correct protein, can resume only once this has taken place. Once again, however, the mRNA is processed differently in the cell nucleus than in the chloroplasts, and for a long time, chloroplast introns seemed to have been an insurmountable hurdle for the correct reading of chloroplast genes in the nucleus.
“But they are actually nothing of the sort”, stresses Ralph Bock, head of the research group. “Our trials have shown that the introns are recognised in the cell nucleus and spliced out, even if not always at exactly the same sites as might have been the case in the chloroplasts.” Functional proteins are formed despite this. It is thought that the introns even help the splicing enzymes by folding themselves into stable RNA structures, thus directing the enzymes to the right locations. At the same time, the RNA structure seems to help the ribosomes find the correct starting point for protein synthesis.
Since the transfer of genes into the cell nucleus is an extremely slow evolutionary process, which has taken nature millions of years, it has not been possible to investigate the underlying mechanism to date. However, researchers have now managed to fast-forward this gene transfer in the laboratory. Because the cells were subjected to high selection pressure, the transference of genes from the chloroplasts into the nucleus became essential for survival, so that it could be made readily visible. It was found that the transfer takes place without the involvement of RNA and that the DNA apparently jumps directly from the cell’s chloroplasts into its nucleus.