Artificial intestine is under development
Advertisement
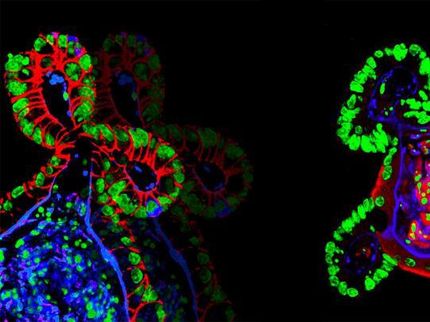
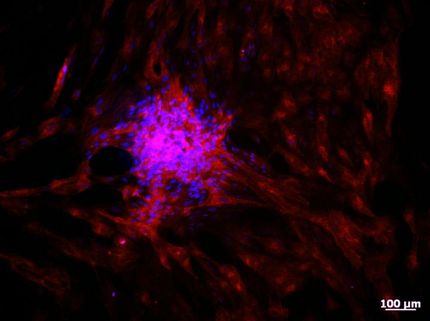
A tiny 3-D collagen "scaffold" developed in a Cornell lab could prove a lifesaver for those who have lost parts of their intestine. John March, associate professor of biological and environmental engineering, is collaborating with a Pittsburgh pediatric surgeon to turn a research tool engineered in his lab into an artificial intestine to be transplanted into children with short bowel syndrome (SBS), a condition connected to Crohn's disease, necrotizing enterocolitis and birth defects.
Unable to absorb food properly, SBS patients must have nutrients administered directly into their veins, which can cause catheter infections and potentially fatal liver toxicity. The majority of children with the condition require intestinal transplantation, a procedure that is limited by a lack of suitable donors and complications from immunosuppressive therapy.
David Hackam of the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine had been exploring SBS treatments using intestinal stem cells but lacked a suitable artificial matrix to host the cell growth.
Meanwhile, March had developed such a matrix, but lacked access to the intestinal stem cells and the expertise in stem cell biology required for it to become a functional intestine.
He is hopeful that by working together, the pair will come up with a "gut tube reactor" that will facilitate the absorption of nutrients. Stem cells from a patient's own intestine would be grown on a hydrogel mold and then be transplanted into the body to act as an artificial intestine. The ambitious project - funded through a $543,571 grant from The Hartwell Foundation - also has an ambitious timeline: three years.
The scientists will start by implanting the tube into mice and coating it with a nutritional formula to test if the mice are able to absorb the nutrients. If successful, they would then move on to pigs, which share greater similarity with humans and have larger abdominal cavities that will facilitate the scale-up of the artificial intestine to a size appropriate for humans.
"The generation of artificial organs represents an absolute holy grail in medical research; a transformative approach for children with short bowel syndrome that could benefit thousands of children by reducing morbidity and mortality," said Frederick Dombrose, president of The Hartwell Foundation.
The tubes will be based on hydrogel scaffolds developed by Cornell graduate student Jiajie Yu and former postdoctoral researcher Jong Hwan Sung, as reported in Lab on a Chip. Their discovery represented a breakthrough in the field, and allowed March's lab to better study drug absorptions and bacteria in the intestine under realistic physiological conditions, rather than relying on two-dimensional cultures or live animal models.
While the original models were done on a tiny scale - about 1 millimeter high and 200 microns across, visible under a scanning electron microscope - March said the new tubes will be much larger.
"It's neat that we are going so quickly into applications of our research," he added.