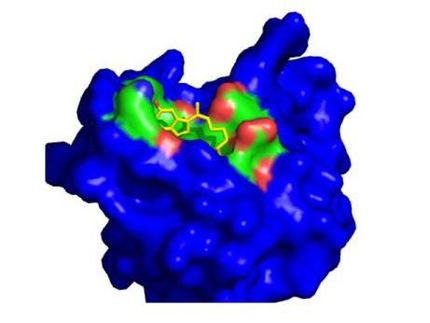
Affitech A/S signs research agreement with UT Southwestern to support further development of its lead antibody drug candidate AT001/r84
Affitech A/S announced that the Company has signed a sponsored research agreement with Dr. Rolf Brekken at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, USA to further understand the mechanism and potential differentiation of Affitech’s lead antibody drug candidate AT001/r84.
The University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas in the USA will conduct certain research regarding Affitech’s anti-VEGF antibody drug candidate AT001/r84, including certain comparative studies with bevacizumab in animal models. Affitech will collaborate with Dr. Rolf Brekken, who has previously published scientific articles on AT001/r84’s effect on cancer in mice.
Affitech will obtain certain rights to intellectual property developed during the course of the research with a view to profitable commercialization of such intellectual property for Affitech’s benefit. The university will perform the research and grant certain rights to such intellectual property.
Most read news
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous

Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous
Last viewed contents
APEIRON Biologics announces financing round for the further development of the COVID-19 drug APN01 - Financing secures further clinical trials and the supply of material for the treatment of COVID-19 patients
NovogeneAIT Singapore and the Genome Institute of Singapore forge Public-Private Partnership - Establishing whole genome sequencing centre in Singapore
Gene that influences the ability to remember faces
Estación_de_Fotobiología_Playa_Unión
E. coli bacteria's defense secret revealed
Felicitex Therapeutics and Selvita Initiate Strategic Collaboration to Target Cancer Quiescence

Faecal Pollution: DNA Uncovers Culprit - CSI and forensics can be used to uncover not only serial killers but also the cause of water pollution
Chinese_Mental_Health_Association
Catalent Invests $7.3 Million in Italy - Expands Softgel Encapsulation and Packaging Capabilities in Support of Consumer Health