Effects of obesity on the brain: first evidence of sex-related differences in the brain’s white matter structure
Previously unknown relationship between body weight and white matter brain structure found exclusively in women
Advertisement
obesity is today one of the most prevalent medical conditions, and has a major impact on health. Recent studies have also shown a relationship between weight and brain structure. Obesity has been associated with a reduced total brain volume and diminished gray matter density. The research team at the Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences in Leipzig, together with the Department of Endocrinology, University Clinic Leipzig, Integrated Research and Treatment Center Adiposity Diseases Leipzig and the University College London have shown a gender-dependent relationship between being overweight and brain structure in the brain’s white matter.
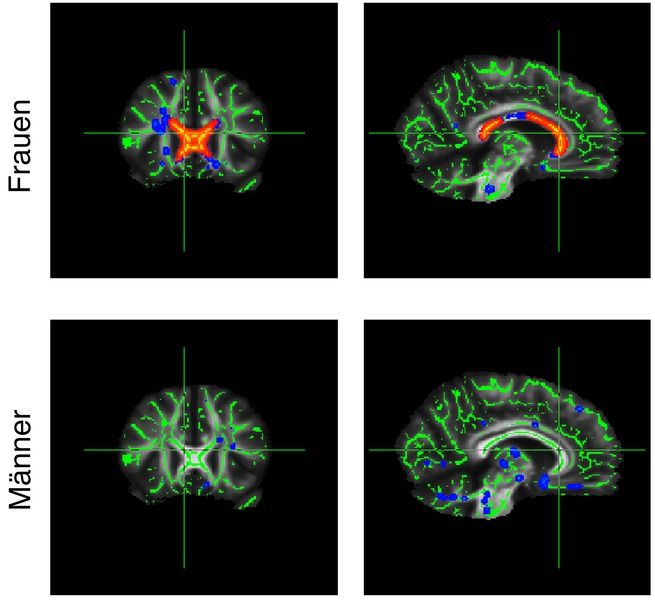
Changes in diffusion in the corpus callosum (marked red) are much greater in obese female participants than in their male counterparts.
© Max Planck Institute for Human Cognitive and Brain Sciences
The researchers investigated the white matter brain structure of lean to obese men and women using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Using this technique, the movement of water molecules (diffusion) can be measured. As this motion is hindered by brain structures like nerve fibers, changes in the white matter brain structures can be investigated.
“Certain changes in the movement of the water molecules in brain tissue can indicate a reduced axonal or myelin density”, says Karsten Mueller, the corresponding author of the study. Such changes were observed in the corpus callosum, a brain structure with 250 million nerve fibers connecting the left and the right hemisphere of the brain. Axons are responsible for transmitting signals in the brain, and myelin is an insulating layer around the axons.
With increasing body mass index (BMI), the mobility of the water changed, both along the nerve fibers and also across them. In both sexes, the researchers found slower diffusion along the nerve fibers. In female participants only, they also found increased movement across the fibers. Both findings could indicate – possibly different – degeneration processes.
The differences in diffusion, which are likewise observed in premature aging of the brain tissue, were more dominant in female participants and covered a greater area of the corpus callosum. This is the first study to show systematic sex-related differences in the relationship between weight and the brain. This could possibly be because connections between the brain hemispheres generally show differences between men and women.
As yet, it is not clear which microstructural changes are actually present. Further studies could bring new insight into this.




























































