Silence Therapeutics Issued New U.S. Patent Covering Fundamental RNA Interference Technology Currently in Several Clinical Trials
New Patent Broadens Company’s Existing Protection of Optimized RNAi Molecules Including Proprietary AtuRNAi Platform
Silence Therapeutics plc announced the issuance of United States patent 7,893,245, titled “Interfering RNA Molecules,” by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO). The issued patent, which represents a continuation of previously issued U.S. Patent Number 7,452,987, covers chemically modified RNAi molecules with defined positional modifications including siRNA molecules that are blunt ended, as well as molecules with one or more overhangs. Importantly, this latest patent broadens Silence’s protection of these RNAi molecules to those with a chemically modified core length between 17 and 29 nucleotides including the company’s portfolio of 25mer siRNA sequences. This patented siRNA technology forms the foundation for AtuRNAi, Silence’s propriety RNAi molecules. Various therapeutics incorporating Silence’s AtuRNAi technology are currently being studied in five ongoing clinical trials conducted by Silence Therapeutics and other industry leaders.
In related intellectual property news, Silence also announces the issuance of United States patent 7,893,243, titled “Composition and Methods of RNAi Therapeutics for Treatment of Cancer and Other Neovascularization Diseases,” by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO). This issued patent is broadly directed to a double stranded, double blunt ended siRNA sequence against the validated cancer target vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). VEGF has been demonstrated to play an important role in the underlying causes of various cancers including abnormal angiogenesis and uncontrolled cell division. The active pharmaceutical ingredient covered by the issued patent is a potent 25mer siRNA, with or without chemical modification, further demonstrating Silence’s continued ability to secure meaningful intellectual property protection for its portfolio of 25mer sequences.
Other news from the department research and development

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
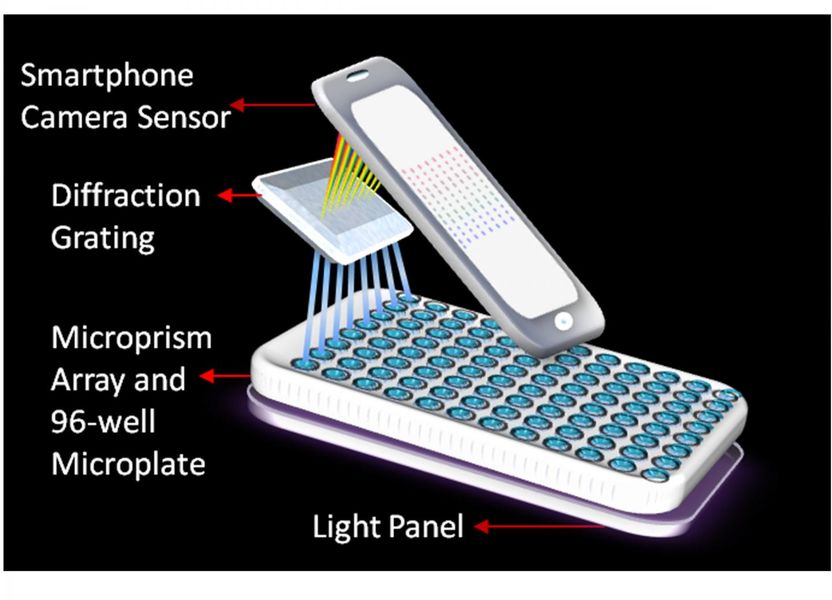
Portable smartphone laboratory detects cancer - WSU portable smartphone laboratory detects cancer

University of Leicester researchers discover new fluorescent silicon nanoparticles - Research may ultimately track the uptake of drugs by the body's cells
Arakis and Vectura announce start of phase IIb trial of NVA237 for COPD
The Crafoord Prize in Polyarthritis 2013

DDBST Dortmund Data Bank Software + Separation Technology GmbH - Oldenburg, Germany
OncoGenex Announces that a Randomized, Investigator-Sponsored Phase 2 Study Evaluating OGX-427 has Received Grant Funding
U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Approves Recombinant Protein Treatment for Tibia Fractures - Wyeth's rhBMP-2/ACS Offers Potential for Improved Fracture Healing























































