Once bitten, twice shy - a temperature switch triggers aversive memory
Neurobiologists can now activate specific nerve cells to study the association between sensations and negative experiences
Prevention is better than cure and avoidance strategies often help to save us from adversity. A child, for example, quickly learns not to touch a hot stove once it burned its fingers. Avoidance behavior is so essential that even the comparatively simple brain of the fruit fly excels in it. If, for example, a fruit fly is presented with a certain odor together with an electric shock, it quickly learns to avoid this particular odor by moving or flying off in the opposite direction. Yet, what actually happens in the brain when two such different stimuli as an odor and an electric shock are linked up with each other to cause a change in behavior? It was precisely this basic phenomenon that scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Neurobiology were determined to track down.
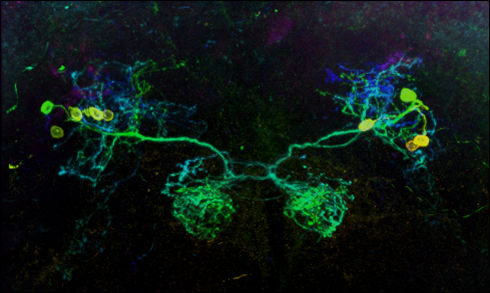
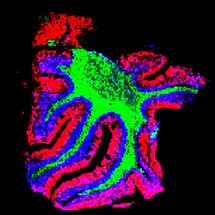
Dopamine-releasing nerve cells which extend into the mushroom-body in the brain of the fly. Neurobiologists now succeeded in showing that three nerve cells establish the association between a negative experience and an odor.
Max Planck Society
The advantages of the fruit fly
The Max Planck Research Group "Behavioral Genetics", led by Hiromu Tanimoto, investigates what happens in the brain of the fruit fly when it learns to avoid something. Given that the fruit fly’s brain is nothing short of minute, one tends to wonder why the scientists investigate this phenomenon in the fruit fly. There are two good reasons for their choice. First of all, the brain of this insect is composed of about one hundred thousand nerve cells and is therefore considerably more straightforward than, say, a human brain which has about one hundred billion nerve cells. The cells responsible for avoidance behavior in the fruit fly can therefore be identified much more readily. What is more, the researchers can use the wide range of genetic tools that is already available for the fruit fly to activate or deactivate certain functions of the animal's brain with great precision.
"We used precisely these qualities to our own advantage", Hiromu Tanimoto explains. The scientists already knew that the connection between an odor and an electric shock occurs inside the mushroom-body - a structure in the brain of the fly that consists of some 2000 nerve cells. It is also clear that the neurotransmitter dopamine enables the flies to learn to associate a potential source of danger with a certain odor. However, until now, it was unclear as to which of the dopaminergic cells are actually responsible for this.
Non-invasive manipulation
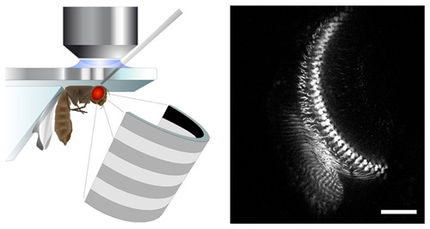
"The problem was that we had to determine which of the nerve cells release dopamine while the flies are moving about and learning to avoid the odor", Tanimoto recapitulates on the study. This is precisely what the scientists have now succeeded in doing. They introduced a "temperature selector" into dopamine-releasing cells that contact cells of the mushroom-body. This stowaway gene stimulated the nerve cells in one set of flies to release dopamine as soon as the room temperature increased slightly. In a second set of flies, a different gene caused the nerve cells to become deactivated once room temperature was increased, no matter what stimulus Tanimoto and his staff presented to the insects. Thus equipped to manipulate, the scientists could demonstrate that the activity of three dopamine-releasing cells is essential for a detected odor to be associated with a negative experience. The decisive role of these three cells was unambiguous: if the cells were temperature-activated while the flies picked up on an odor, then the insects learned to avoid the odor - even without the electric shock that constituted the negative association with the odor.
"We can now actually examine the function of individual nerve cells in an active and behaving animal. This opens up new horizons", Yoshinori Aso, who is visibly delighted with the outcome of his experiment, adds. Step by step, the scientists now plan to get to the bottom of how experiences are linked to each other and how behavior modification develops.
Original publication: Yoshinori Aso, Igor Siwanowicz, Lasse Bräcker, Kei Ito, Toshihiro Kitamoto, Hiromu Tanimoto; "Specific dopaminergic neurons for the formation of labile aversive memory"; Current Biology, online publication, 15. July 2010