New medical weapons to protect against anthrax attacks
Advertisement
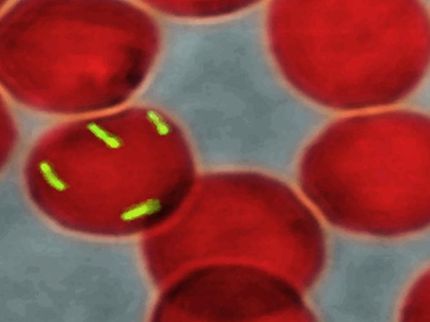
The 2001 anthrax attacks in the United States are fostering development of a new generation of vaccines, antibiotics, and other medications to protect people against the potentially deadly bacteria in any future bioterrorist incident. That's the conclusion of a sweeping overview of scientific research on medical technology to combat the anthrax threat. It appears in the Journal of medicinal chemistry .
In the article, Dimitrios Bouzianas notes that several existing antibiotics are available to combat an anthrax infection. However, the emergence of artificially engineered B. anthracis strains, resistant to multiple antibiotics (including the front-line agents ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, and beta-lactam antibiotics) has prompted researchers to pursue additional therapeutic options. Such alternatives include small molecules and antibodies against toxins that the lethal bacteria secrete. Passive immunization using a polyclonal or a high-affinity monoclonal antibody may offer adjunctive value to antibiotic therapy. Today's drug arsenal has another weakness: no medications available to fight the dangerous toxin that can circulate in a person's blood when antibiotic treatment begins after the disease has taken hold. Therefore, there is an urgent need for the discovery of antitoxin agents that would be effective at the end stage of anthrax.
Bouzianas describes promising new treatments now in various stages of development. They include a new genre of anthrax vaccines that would be more effective and yet require fewer doses than current vaccines. Among them: A long-sought inhalable vaccine that people might self-administer without a needle. Importantly, this powered vaccine would not require refrigeration and would have a long shelf life — ideal for the strategic drug stockpiles kept on hand for rapid distribution in case of national emergencies. Also on the horizon: New antibiotics that are less likely to encounter resistance and medicines that can block the effects of anthrax toxin. Because anthrax is rare as a natural disease in humans, the development of new treatment modalities is seriously hampered by the difficulty in demonstrating their effectiveness in humans.
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous

Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous