“Multi Organ Model” - Animal-free alternative for pharmacokinetics research
Dynamic42 and research partners present three-organ system to reduce animal testing
Organ-on-chip specialist Dynamic42 and ESQlabs, experts in digital life sciences solutions, have successfully developed a three-organ system, in close collaboration with Consumer Health Division of Bayer, and the Placenta Lab at Jena University Hospital. The platform has the potential to significantly reduce animal testing using Organ-on-chip (OoC) technology and interactive computational software. The aim of the one-year pilot project was to collect clinically relevant data, crucial for the evaluation of new drug candidates in preclinical research. The results of the project have now been published in Frontiers in Pharmacology journal.

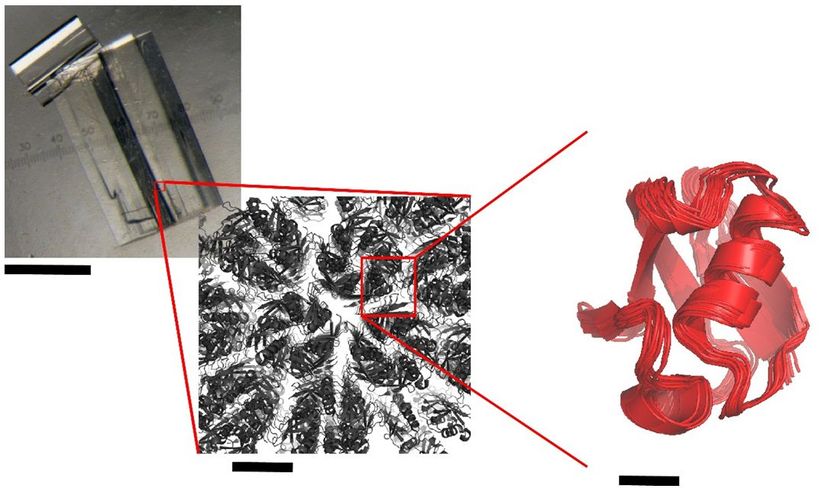
Three-organ system with intestine, liver and placenta on a biochip. The distribution pathway of the drug in all three organs is shown in magenta and the apical drug application in the intestinal model is shown in blue.
Dynamic42 GmbH
The project investigated whether certain drugs could cross the blood-placental barrier in pregnant women – a group of people who are rarely included in clinical trials due to ethical and practical restrictions. A particular focus was on the investigation of drugs during pregnancy, especially corticosteroids such as prednisone, as there are limited data available on pharmacokinetics and safety in this area. Conventional preclinical models, including animal studies, do not provide sufficient information on the drug exposure of the mother and the unborn child.
Three-organ model improves prediction of drug response
To address the existing gap in preclinical drug research, Dynamic42 has further developed the potential of its existing platform, which is based on the so-called “organ-on-chip” technology. The developed platform represents the three main human tissues involved in drug utilization – liver, intestine and placenta. An integrated pump system ensures that the cell culture medium circulates between the tissues, thus enabling a realistic simulation of substance distribution. The coupled digital analysis of the data generated in the platform enables transfer to human conditions. Using the drug prednisone as a model substance, the system simulates the absorption, metabolism and transfer of the drug via the placenta.
Simulation with digital twin technology
The use of digital twin technology is a promising approach to improving drug safety and efficacy. With the help of computer models that realistically depict biological processes, both acute and long-term drug effects can be simulated. ESQlabs integrates experimental data from the multi-organ platform into mathematical models to precisely predict the distribution and metabolism of drugs in pregnant women. This contributes to a better evaluation of dose-response relationships and risk assessment.
Animal-free alternative for pharmacokinetics research
Although animal testing is often mandatory in the preclinical phase of new drug development, in some cases it can be difficult to transfer the results from animals to humans. The developed platform represents a promising alternative to animal testing and makes an important contribution to the understanding of drug behavior during pregnancy. It can also support the early assessment of drug safety in vulnerable populations. These results underline the potential of the system to simulate complex pharmacological processes in vitro and thus enable more accurate predictions of drug safety and efficacy.
Quotes from the partners
“We have created an exciting new way to combine MPS in a multi-organ setting with in silico predictions. With this platform, we can take drug safety and efficacy assessment to a whole new level, providing valuable data for the development of safe and effective therapies,” said Dr. Martin Raasch, CEO of Dynamic42.
“At ESQlabs, we specialize in bridging the gap between wet-lab data and computational modeling through our digital twins’ technologies for translational research. By integrating in-silico simulations with multi-organ MPS platforms, we elevate preclinical testing to new levels of precision and reliability. This collaborative pilot project with Dynamic42, Bayer, and the Placenta Lab illustrates how we can reduce animal testing and deepen our understanding of drug behavior in complex, human-relevant systems,” says Dr. Christian Maass, BU Lead MPSlabs.
“The Placenta Lab is active in a wide range of research topics related to human reproduction and pregnancy. This collaboration is a major milestone for the development of new mechanisms to study the placental barrier and its bidirectional selective transport in humans,” says Priv.-Doz. Dr. Diana Morales Prieto, deputy director and scientific group leader of the Placenta Lab.
“It has been an important concern of Bayer for years to minimize animal testing according to the 3R principles (Reduce, Refine and Replace). In the joint project with scientists from ESQlabs, Dynamic42 and the Placenta Lab, we were able to develop new approaches to further minimize animal testing. At the same time, we have gained more accurate and reliable data on drug safety and efficacy,” says Assoc. Prof. Ramy Ammar, Science Innovation Director, Front End Innovation, Consumer Health Division of Bayer. “We are pleased to have taken such an important step in the development of alternative testing methods.”
Other news from the department business & finance
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Something is happening in the life science industry ...
This is what true pioneering spirit looks like: Plenty of innovative start-ups are bringing fresh ideas, lifeblood and entrepreneurial spirit to change tomorrow's world for the better. Immerse yourself in the world of these young companies and take the opportunity to get in touch with the founders.