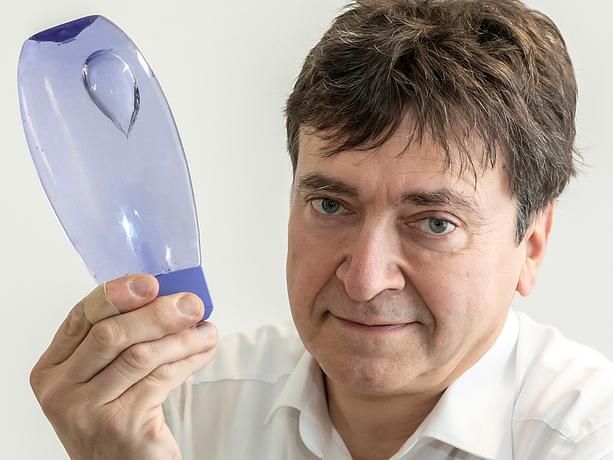
Removing microplastics with engineered bacteria
Researchers altered bacteria found in wastewater treatment, where microplastics can enter environment
microplastics can go right through wastewater treatment plants, and researchers have engineered bacteria commonly found in there to break down this pollution before it can persist in the environment.
Researchers from the University of Waterloo added DNA to several species of bacteria found in wastewater, allowing them to biodegrade polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a common plastic found in carpet, clothing and containers for food and beverages.
PET plastics take hundreds of years to degrade in the environment. Over time, they break down into microplastics, pieces of plastic less than 5 mm long, which enter the food chain. Chemicals in these plastics are associated with insulin resistance, cancer and decreased reproductive health.
“Think of these bacteria that already exist in water systems to clean up microplastics as biorobots that can be programmed to get the job done,” said Dr. Marc Aucoin, a professor in the Department of Chemical Engineering. “Microplastics in water also enhance the spread of antibiotic resistance, so this breakthrough could also address that concern.”
The researchers use a natural process referred to as “bacterial sex,” where bacteria share genetic material with each other when multiplying. It enables the introduction of a new trait into the target bacteria, giving them the ability to break down microplastics.
“As next steps, we will use modelling to understand how well the bacteria transfer the new genetic information under different environmental conditions and thus how effectively they can break down the plastics,” said Dr. Brian Ingalls, a professor in the Department of Applied Mathematics. “The long-term vision is to break down microplastics in wastewater treatment plants at scale.”
While the researchers will start with wastewater facilities, they also hope to find ways to clean up the plastic waste accumulating in oceans.
"We will assess the risks of using engineered, plastic-eating bacteria in the natural environment" said Aaron Yip, a PhD student in the Department of Chemical Engineering. "Right now, microplastic degradation in wastewater treatment plants is a safer application to target. Many of these facilities are already designed to neutralize bacteria in wastewater, which would kill any engineered bacteria prior to discharging water back into the environment.”
Original publication
Most read news
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Muscle_weakness
Gallstone
Institute_for_Research_into_Cancer_of_the_Digestive_System
Psilocin
Indeterminate_growth

Tiny algae ideal for sniffing out nutrient pollution in water
Atony