Gut microbiota and antibiotics: Missing puzzle piece discovered
HIRI scientists identify small RNA that influences the sensitivity of the intestinal pathogen Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron to certain antibiotics
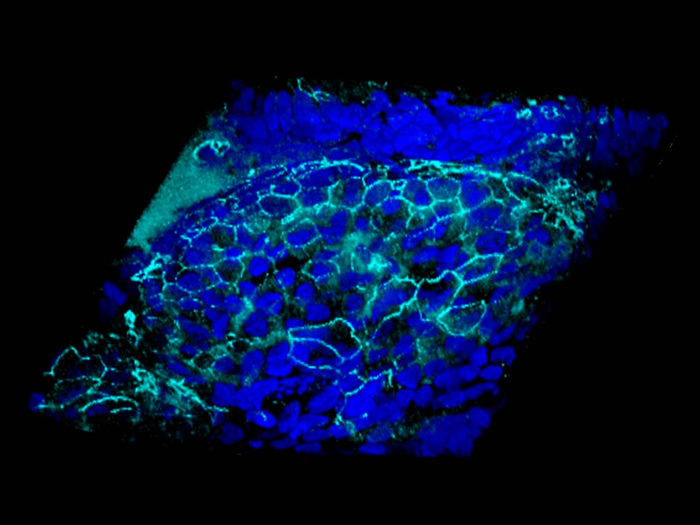
The intricacies of how intestinal bacteria adapt to their environment have yet to be fully explored. Researchers from the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) in Würzburg and the University of California, Berkeley, USA, have now successfully closed a gap in this knowledge: They have identified a small ribonucleic acid (sRNA) that affects the susceptibility of the gut pathogen Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron to specific antibiotics. The findings, published today in the journal Nature Microbiology, could serve as the foundation for novel therapies addressing intestinal diseases and combating antibiotic resistance.
The gut, a complex ecosystem of numerous microorganisms, plays a pivotal role in human well-being. Factors like dietary changes, medications, or bile salts can influence the microbiota, impacting health. Among the prevalent intestinal bacteria in humans are Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. These gut microbes play a role in breaking down polysaccharides during digestion, contributing to human health. Yet they can also promote infections when the ecosystem is disbalanced, such as after antibiotic treatment. However, the molecular mechanisms enabling these gut microbes to adapt to their environment remain largely unknown.
“My group and I want to understand how Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron adapt to changing conditions in the gut,” says Alexander Westermann, summarizing the goal of the study published today in the journal Nature Microbiology. The initiator of the investigation is a research group leader at the Helmholtz Institute for RNA-based Infection Research (HIRI) in Würzburg, a site of the Braunschweig Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research (HZI) in cooperation with the Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU).
To illuminate the transcription networks in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, HIRI scientists collaborated with researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, USA, to map transcription units and profile their expression under different experimental conditions. Comparing this gene expression information with literature-derived fitness data from genetically engineered bacterial variants, the research team was able to gain a holistic view of the regulatory networks and the functional role of sRNAs in bacterial adaptation. “Our findings offer new insights into the complex interplay between environmental cues, gene expression, and bacterial fitness,” says Westermann, who also holds a professorship at the JMU.
Small RNA regulates antibiotic sensitivity
The researchers, by studying the nucleic acid content of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, identified a specific regulatory RNA molecule—a small RNA (sRNA)—that influences the bacterium's sensitivity to tetracycline antibiotics. “With the discovery of the sRNA MasB and its role in modulating antibiotic sensitivity, we have revealed a previously uncharacterized regulatory mechanism,” says first author and postdoctoral researcher Daniel Ryan. The results provide information about the influence of antibiotic treatments on members of the microbiota. On this basis, new strategies for preventing antibiotic-induced collateral damage to beneficial bacteria could be developed and therapeutics improved.
The findings represent a valuable asset for the microbiome community: The comprehensive transcriptome atlas, which is publicly available through the web browser “Theta-Base”, presents the opportunity to study more sRNAs and explore their functions in this context. “The RNA biology of Bacteroides and other members of the gut microbiota is still poorly understood. Research endeavors of this kind lay the groundwork for future investigations, offering a foundational resource for further exploration,” says Westermann.
Original publication
Daniel Ryan, Elise Bornet, Gianluca Prezza, Shuba Varshini Alampalli, Taís Franco de Carvalho, Hannah Felchle, Titus Ebbecke, Regan J. Hayward, Adam M. Deutschbauer, Lars Barquist, Alexander J. Westermann; "An expanded transcriptome atlas for Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron reveals a small RNA that modulates tetracycline sensitivity"; Nature Microbiology, 2024-3-25
Original publication
Daniel Ryan, Elise Bornet, Gianluca Prezza, Shuba Varshini Alampalli, Taís Franco de Carvalho, Hannah Felchle, Titus Ebbecke, Regan J. Hayward, Adam M. Deutschbauer, Lars Barquist, Alexander J. Westermann; "An expanded transcriptome atlas for Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron reveals a small RNA that modulates tetracycline sensitivity"; Nature Microbiology, 2024-3-25
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
U.S. Army funds TNO and to-BBB to investigate protecting soldier’s brains from nerve agents
GATC Biotech opens office in Sweden

Study finds clear differences between organic and non-organic milk and meat

Mapping chemicals in the skin - Reducing animal experiments with chemical imaging
New receptor found on scavenger cells - How adenoviruses invade the immune system of mice

Stress factor regulates obesity - Researchers find new link to cell's recycling system

Lab supplies out of the 3D printer - LAUDA invests in Better Basics start-up
Monitoring the corrosion of bioresorbable magnesium - Better prediction of degradation rate of magnesium implants

Closer connection to nature may affect child's health via breastmilk - Green environments in residential areas impact the composition of sugar molecules in breastmilk