Innovative microscopy technique reveals secrets of lipid synthesis inside cells
Two-color infrared photothermal microscopy (2C-IPM) opens new avenues for long-term study of lipid metabolism in living cells
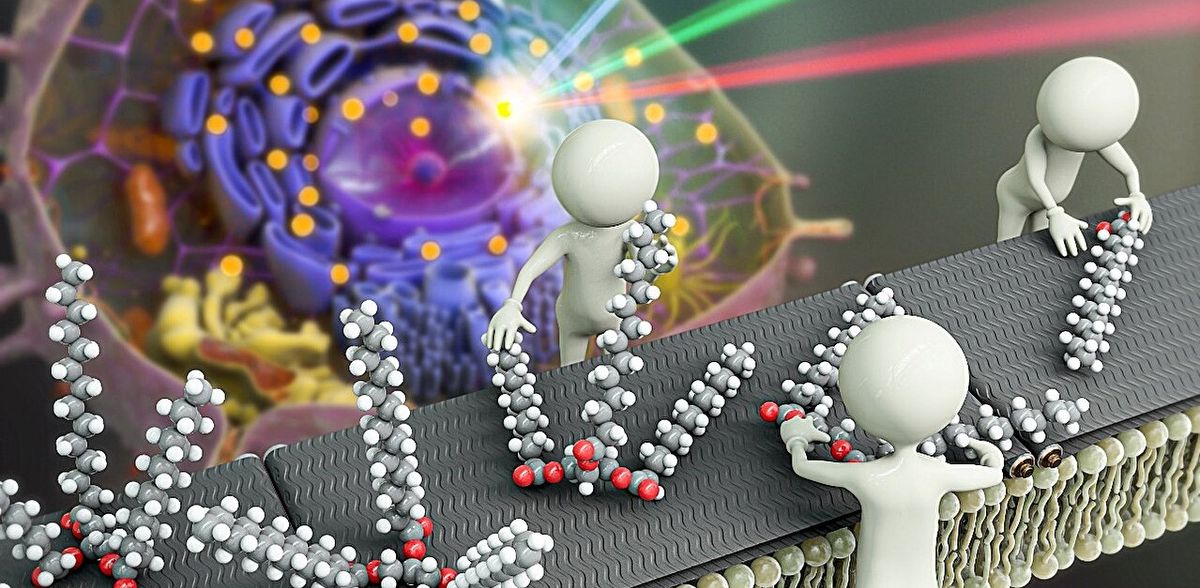
South Korean researchers led by Director CHO Minhaeng at the IBS Center for Molecular Spectroscopy and Dynamics (IBS CMSD) made a pivotal discovery in the field of cellular microscopy. The team has successfully developed Two-Color Infrared Photothermal Microscopy (2C-IPM), a novel technology designed to investigate neutral lipids within lipid droplets of living cells. This new microscopy can be used with isotope labeling, which allows for the detailed monitoring of neutral lipid synthesis within individual lipid droplets.
Lipid droplets (LDs) are structure that consists of pockets of neutral lipids (triglycerides) encapsulated in a monolayer of phospholipids. They have long been thought of as relatively uninteresting organelles, whose only purpose is to store excess energy in the form of neutral lipids. However, recent studies indicate these droplets actually are dynamic players in various cellular metabolic activities. It was found they are actively involved in regulating lipid toxicity and cell communication, as well as their correlation with prevalent diseases like obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Understanding the functions of LDs is thus imperative for the diagnosis and treatment of these conditions.
Researchers have traditionally stained the cells with lipophilic dyes and employed fluorescence microscopy to study LDs within cells. However, this method has several significant limitations. First is photobleaching of the dyes, which restricts the observation duration of the LDs to very short time windows. Another limitation is the fluorescent dyes themselves. The currently used fluorescent dyes simply target the hydrophobic environment within LDs, utilizing unspecified binding mechanisms. As such, they are incapable of accurately analyzing the composition and quantity of neutral lipids.
Unlike previous methods that relied on fluorescent microscopy, the new 2C-IPM technology uses an infrared (IR) spectroscopic method and does not require the use of fluorescent dyes. The new method monitors neutral lipids within LDs directly by detecting changes in IR absorbance. Importantly, this advantage allows researchers to observe the synthesis of neutral lipids within individual LDs in living cells over a long period.
Employing the newly developed method, the research team studied the synthesis of neutral lipids in cells when they were exposed to excess fatty acids. The researchers were able to distinguish freshly synthesized neutral lipids from pre-existing neutral lipids within cells by subjecting deuterium-labeled fatty acids, which have distinct spectroscopic properties from non-deuterated forms. The analysis results verified excess fatty acids caused lipid toxicity, and cells respond by increasing the synthesis of neutral lipids.
The lead author, researcher PARK Chanjong, remarked, "This study serves as a fundamental example demonstrating the possibility of long-term research on lipid droplets and internal neutral lipids in living cells. The analytical method established in this research can be applied to the diagnosis and treatment of diseases closely associated with lipid metabolism, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease."
Director CHO Minhaeng commented, "By successfully observing the process of neutral lipid synthesis in living cells, we have laid a new foundation for studying the functions of lipid droplets within cells at the molecular level. This method is expected to be widely used in the investigation of various cellular metabolic phenomena."
Original publication
Most read news
Original publication
Chanjong Park, Jong Min Lim, Seok-Cheol Hong, Minhaeng Cho; "Monitoring the synthesis of neutral lipids in lipid droplets of living human cancer cells using two-color infrared photothermal microscopy"; Chemical Science, Volume 15, 2024
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Cell Analysis
Cell analyse advanced method allows us to explore and understand cells in their many facets. From single cell analysis to flow cytometry and imaging technology, cell analysis provides us with valuable insights into the structure, function and interaction of cells. Whether in medicine, biological research or pharmacology, cell analysis is revolutionizing our understanding of disease, development and treatment options.

Topic World Cell Analysis
Cell analyse advanced method allows us to explore and understand cells in their many facets. From single cell analysis to flow cytometry and imaging technology, cell analysis provides us with valuable insights into the structure, function and interaction of cells. Whether in medicine, biological research or pharmacology, cell analysis is revolutionizing our understanding of disease, development and treatment options.
Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!

Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!