AI identifies antimalarial drug as possible osteoporosis treatment
Osteoporotic mice treated with the drug had significantly improved bone density
artificial intelligence has exploded in popularity and is being harnessed by some scientists to predict which molecules could treat illnesses, or to quickly screen existing medicines for new applications. Researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have used one such deep learning algorithm, and found that dihydroartemisinin (DHA), an antimalarial drug and derivative of a traditional Chinese medicine, could treat osteoporosis as well. The team showed that in mice, DHA effectively reversed osteoporosis-related bone loss.
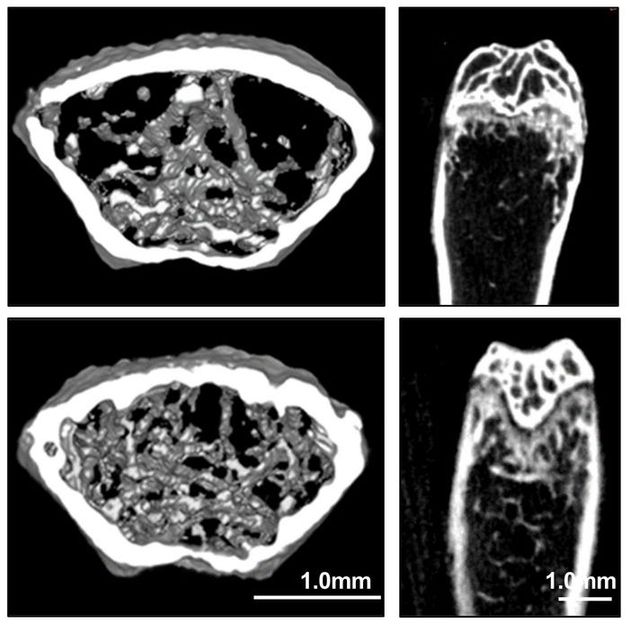
Osteoporotic mice treated with dihydroartemisinin (DHA) had significantly improved bone density (bottom) compared to controls (top).
Adapted from ACS Central Science, 2023, DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.3c00794
In healthy people, there is a balance between the osteoblasts that build new bone and osteoclasts that break it down. But when the “demolition crew” becomes overactive, it can result in bone loss and a disease called osteoporosis, which typically affects older adults. Current treatments for osteoporosis primarily focus on slowing the activity of osteoclasts. But osteoblasts — or more specifically, their precursors known as bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMMSCs) — could be the basis for a different approach. During osteoporosis, these multipotent cells tend to turn into fat-creating cells instead, but they could be reprogrammed to help treat the disease. Previously, Zhengwei Xie and colleagues developed a deep learning algorithm that could predict how effectively certain small-molecule drugs reversed changes to gene expression associated with the disease. This time, joined by Yan Liu and Weiran Li, they wanted to use the algorithm to find a new treatment strategy for osteoporosis that focused on BMMSCs.
The team ran the program on a profile of differently expressed genes in newborn and adult mice. One of the top-ranked compounds identified was DHA, a derivative of artemisinin and a key component of malaria treatments. Administering DHA extract for six weeks to mice with induced osteoporosis significantly reduced bone loss in their femurs and nearly completely preserved bone structure. To improve delivery, the team designed a more robust system using injected, DHA-loaded nanoparticles. Bones of mice with osteoporosis that received the treatment were similar to those of the control group, and the treatment showed no evidence of toxicity. In further tests, the team determined that DHA interacted with BMMSCs to maintain their stemness and ultimately produce more osteoblasts. The researchers say that this work demonstrates that DHA is a promising therapeutic agent for osteoporosis.
Original publication
Ruoxi Wang, Yu Wang, Yuting Niu, Danqing He, Shanshan Jin, Zixin Li, Lisha Zhu, Liyuan Chen, Xiaolan Wu, Chengye Ding, Tianhao Wu, Xinmeng Shi, He Zhang, Chang Li, Xin Wang, Zhengwei Xie, Weiran Li, Yan Liu; "Deep Learning-Predicted Dihydroartemisinin Rescues Osteoporosis by Maintaining Mesenchymal Stem Cell Stemness through Activating Histone 3 Lys 9 Acetylation"; ACS Central Science, 2023-10-18
Most read news
Original publication
Ruoxi Wang, Yu Wang, Yuting Niu, Danqing He, Shanshan Jin, Zixin Li, Lisha Zhu, Liyuan Chen, Xiaolan Wu, Chengye Ding, Tianhao Wu, Xinmeng Shi, He Zhang, Chang Li, Xin Wang, Zhengwei Xie, Weiran Li, Yan Liu; "Deep Learning-Predicted Dihydroartemisinin Rescues Osteoporosis by Maintaining Mesenchymal Stem Cell Stemness through Activating Histone 3 Lys 9 Acetylation"; ACS Central Science, 2023-10-18
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.























































