How a metabolite causes inflammation and disease
The accumulation of the metabolite fumarate in the mitochondrion, the powerhouse of a cell, can cause inflammation associated with diseases such as cancer and autoimmune diseases
A new study shows for the first time a connection between a mitochondrial metabolite and the activation of an inflammatory response. mitochondria are functional units of our cells that fulfil important tasks, i.e. chemical reactions, for the functioning of the cell. One of these tasks is the production of energy that is necessary for cell growth and reproduction. If certain chemical reactions in the mitochondrion change, diseases occur. For example, deficiencies in fumarate hydratase (FH) in the Krebs cycle, one of the most important metabolic pathways in mitochondria, cause an aggressive form of kidney cancer in humans. FH loss leads to the accumulation of the molecule fumarate, which contributes to the development of cancer. For this reason, fumarate is called an oncogenic metabolite, or “oncometabolite” for short.
The research team led by Alexander von Humboldt Professor Dr Christian Frezza, formerly at the University of Cambridge (United Kingdom) and now at the CECAD Cluster of Excellence for Aging Research at the University of Cologne, has now developed a new mouse and cell model together with the research group led by Professor Prudent of the University of Cambridge to deepen the understanding of aggressive kidney cancer. In the models, the silencing of the fumarate hydratase gene can be temporally controlled by the scientists. Using a combination of high-resolution imaging techniques and precise biochemical experiments, the scientists have shown that fumarate causes mitochondrial damage. This in turn releases the genetic material of the mitochondria in small vesicles called mitochondrial-derived vesicles. These vesicles filled with mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and RNA (mtRNA) trigger an immune reaction that eventually leads to inflammation. The study titled “Fumarate induces vesicular release of mtDNA to drive innate immunity” was published in Nature.
“Our study shows for the first time a correlation between a mitochondrial metabolite and the onset of inflammation, which could be the trigger for cancer and autoimmune diseases,” said Professor Frezza. “Based on these findings, we can now work on new approaches to treat patients, which will hopefully lead to the development of new therapeutic strategies to treat cancer patients in the future.”
In addition, a group at Trinity Biomedical Sciences Institute in Dublin led by Professor Luke O’Neill in collaboration with Christian Frezza’s research group has described a similar mechanism in macrophages. Macrophages are cells of the body that are responsible for eliminating harmful microbes. Here, the researchers found that mitochondrial RNA released by the macrophages’ mitochondria, rather than DNA, is the main trigger of inflammation. The study “Macrophage fumarate hydratase restrains mtRNA-mediated interferon production” was also published in the journal Nature.
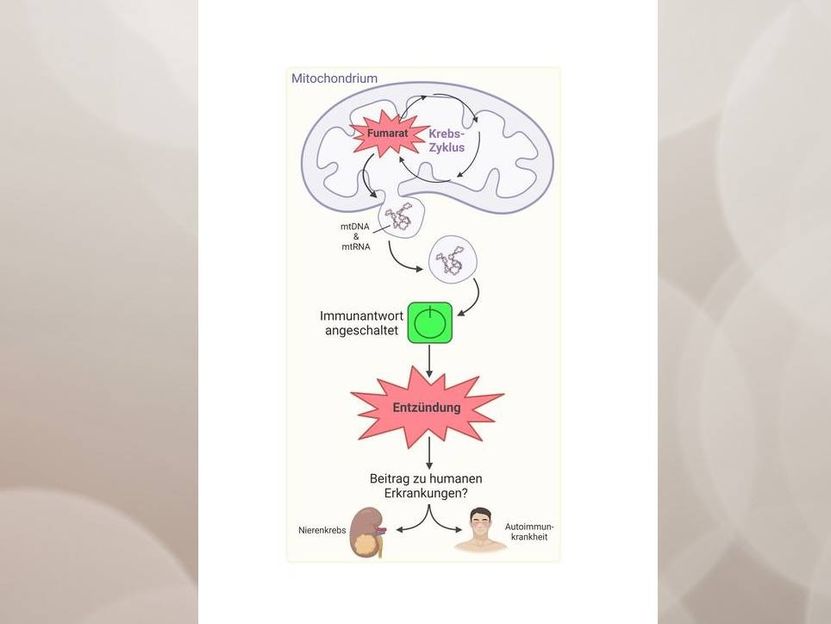
The accumulation of the oncometabolite fumarate in mitochondria leads to the secretion of genetic material (mtDNA and mtRNA) in vesicles. This leads to activation of the immune system and inflammation, which can cause human diseases.
Created with BioRender.com / Universität Köln