Engineered proteins: A future treatment option for COVID-19
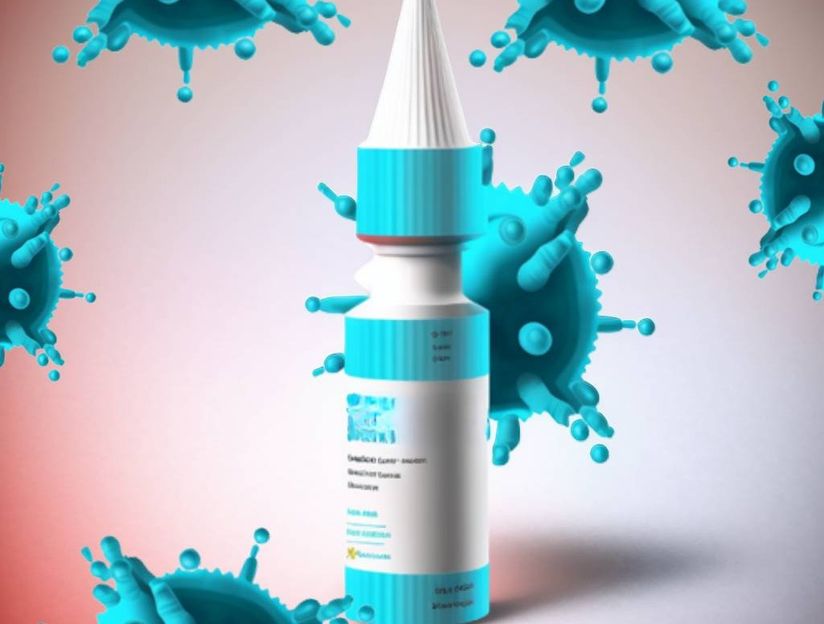
Newly engineered proteins called DARPins can decrease the presence of COVID-19 in the airways and be delivered as a nasal spray
Covid-19 has had a lasting global health impact that continues to challenge the health care system. As the coronavirus continues to mutate, the current COVID-19 prevention strategies are plagued with supply chain disruptions, high vaccine manufacturing costs and inconvenient vaccine administration methods. In a study published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology, the lab of Zhilei Chen, PhD, at Texas A&M University School of Medicine engineered two small and specifically targeted proteins that could be administered as a nasal spray to protect against and treat COVID-19.

Symbolic image
Computer-generated image
The proteins were templated on the designed ankyrin repeat protein (DARPin), a synthetic scaffold inspired by a class of binding proteins commonly found in nature. Compared to conventional antibody-based drugs, DARPins are less prone to “go bad” during prolonged storage at moderate-to-high temperatures and can be made in large quantities at low cost, making DARPins potentially much more affordable. In addition, since DARPins are about one-eighth the size of an antibody, they have the capacity to access specific therapeutically important “hot spots” on a disease-related protein with greater precision.
In this study, the researchers created two DARPin molecules that assemble in groups of three and block the interaction between the primary protein used by the COVID-19 virus to enter cells and its partner on host cells, thus stopping the virus in its tracks. When delivered into the nose of animal models with the COVID-causing virus, the DARPins reduced the amount of virus that accumulate in the airways by up to 100-fold and significantly reduced disease progression. What’s more, the DARPins were effective not only against the original variant, but also all of the newer COVID-causing variants, including the omicron strain. The researchers attribute the broad effectiveness of the DARPins to their engineering design, which resulted in DARPins able to mimic a key interface on the cellular receptor needed by the virus to enter cells.
“This study offers the possibility of an on-demand nasal spray able to tackle COVID either before or after virus exposure,” Chen said. The team’s discovery provides another, potentially lower-cost therapeutic option for those who cannot receive traditional vaccines or are considered high risk.
The DARPin molecules were engineered by Vikas Chonira, PhD, with assistance from Rudo Simeon, PhD, both postdoctoral fellows in the Chen lab. This research is part of a larger collaborative effort that included Michael S. Diamond, MD, PhD, from Washington University; Peter D. Kwong, PhD, from the National Institutes of Health; and Zhiqiang An, PhD, from University of Texas Health Houston. Funding for the Chen lab is provided by the NIH New Innovator Award.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents

Hettich successfully completes acquisition of Kirsch Medical
Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard - Cambridge, USA

Did Neanderthals already have a fatty liver? - What archeogenetics tells us about liver steatosis in ancient and modern humans
Yellow pigment keeps social amoebae together - "Amoebae produce a variety of natural substances that could be interesting, for example, for the development of new medicines"

Phenomenex Ltd. - Aschaffenburg, Germany