Fertilizing the ocean to store carbon dioxide
Iron-based fertilizer, engineered into nanoparticles, could help store excess carbon dioxide in the ocean
The urgent need to remove excess carbon dioxide from Earth’s environment could include enlisting some of our planet’s smallest inhabitants, according to an international research team led by Michael Hochella of the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.
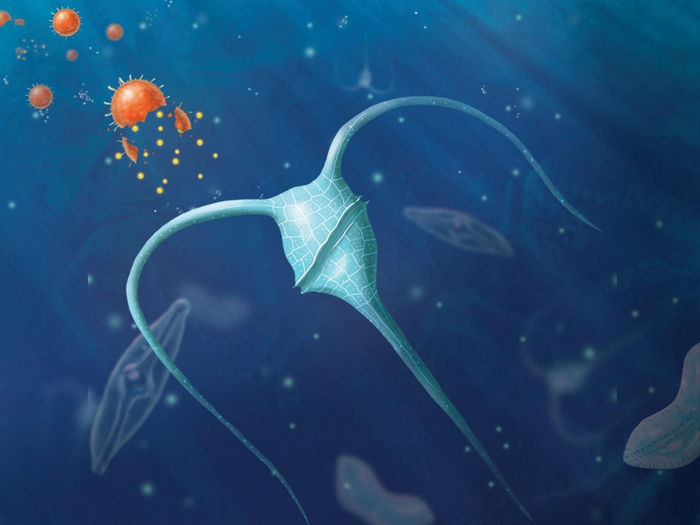
Seeding the oceans with nano-scale fertilizers could create a much-needed, substantial carbon sink.
Illustration by Stephanie King | Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Hochella and his colleagues examined the scientific evidence for seeding the oceans with iron-rich engineered fertilizer particles near ocean plankton. The goal would be to feed phytoplankton, microscopic plants that are a key part of the ocean ecosystem, to encourage growth and carbon dioxide (CO2) uptake. The analysis article appears in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
“The idea is to augment existing processes,” said Hochella, a Laboratory fellow at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. “Humans have fertilized the land to grow crops for centuries. We can learn to fertilize the oceans responsibly.”
In nature, nutrients from the land reach oceans through rivers and blowing dust to fertilize plankton. The research team proposes moving this natural process one step further to help remove excess CO2 through the ocean. They studied evidence that suggests adding specific combinations of carefully engineered materials could effectively fertilize the oceans, encouraging phytoplankton to act as a carbon sink. The organisms would take up carbon in large quantities. Then, as they die, they would sink deep into the ocean, taking the excess carbon with them. Scientists say this proposed fertilization would simply speed up a natural process that already safely sequesters carbon in a form that could remove it from the atmosphere for thousands of years.
“At this point, time is of the essence,” said Hochella. “To combat rising temperatures, we must decrease CO2 levels on a global scale. Examining all our options, including using the oceans as a CO2 sink, gives us the best chance of cooling the planet.”
Pulling insights from the literature
In their analysis, the researchers argue that engineered nanoparticles offer several attractive attributes. They could be highly controlled and specifically tuned for different ocean environments. Surface coatings could help the particles attach to plankton. Some particles also have light-absorbing properties, allowing plankton to consume and use more CO2. The general approach could also be tuned to meet the needs of specific ocean environments. For example, one region might benefit most from iron-based particles, while silicon-based particles may be most effective elsewhere, they say.
The researchers’ analysis of 123 published studies showed that numerous non-toxic metal-oxygen materials could safely enhance plankton growth. The stability, Earth abundance, and ease of creation of these materials make them viable options as plankton fertilizers, they argue.
The team also analyzed the cost of creating and distributing different particles. While the process would be substantially more expensive than adding non-engineered materials, it would also be significantly more effective.