Tears instead of Blood
Sensor with separation capability: diagnosing jaundice using tear fluids
Human tear fluids contain many proteins, metabolites, and other molecules whose concentrations change significantly with certain diseases. A research team has now developed a handy test kit for tears that can identify patients with jaundice. Their success is based on a hybrid sensor that simultaneously removes impurities from the sample. This approach could provide new methods for early detection and diagnosis based on complex bodily fluids, as the team reported in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
© Wiley-VCH
One particular advantage of tear fluid diagnosis is that samples can be collected in a comfortable and non-invasive manner. A method called surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) is a suitable candidate for the analysis of the biomolecules obtained. The Raman effect is a phenomenon in which light striking materials causes characteristic vibrations and rotations of molecular fragments. The resulting shift in the frequency of the scattered light gives a molecular “fingerprint”. If the analyte molecules are in contact with a metal surface (hotspots), the Raman signals are amplified enough to reach the ultra-sensitivity required for tear diagnostics. Labeling the analytes is unnecessary. Compact Raman hand devices would be available for direct diagnosis in the field. The problem is in finding suitable SERS sensors. Current sensors are quickly deactivated by deposition of tear components. Is there a way to make this work without complex sample preparation?
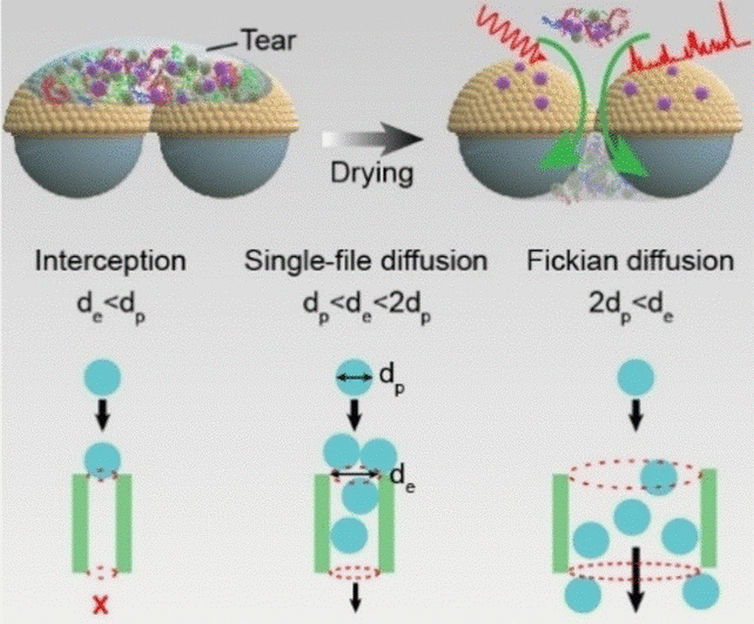
In fact, there is. A team led by Yun Feng (Peking University Third Hospital), Zhou Yang (University of Science and Technology Beijing), and Tie Wang (Tianjin University of Technology and Chinese Academy of Sciences Beijing), has demonstrated this with their novel matchbox-sized diagnostic test kit. At its heart lies a hybrid film. A layer of symmetrically arranged silicon dioxide nanospheres is coated with a whisper-thin layer of gold, onto which is deposited a layer of gold nanoparticles that act as SERS hotspots. The target molecules bind to the gold and are held fast to the surface, while smaller tear components slip through the gaps between the silicon dioxide nanoparticles onto an absorbent layer below. The pore diameters can be adjusted by changing the size of the nanospheres to selectively separate out the disruptive primary components of tears (albumin, lysozyme, IgG, and peroxidase). The film, called SiO2@Au@AuNPs, is sandwiched between two glass supports and enclosed in a housing. A tip protrudes from the device to collect tear fluid from the corner of the eye. The SERS analysis occurs through a window on top of the device.
The team was able to successfully identify patients with jaundice—a metabolic disorder associated with liver and gall bladder diseases. The bile pigment bilirubin is not properly excreted from the body, becomes concentrated, and can be found in tear fluid. Bilirubin binds strongly to the sensor’s gold and can be detected with great sensitivity by its SERS signal.
Original publication
Original publication
Dr. Weidong Zhao et al.; A Separation-Sensing Platform Performing Accurate Diagnosis of Jaundice in Complex Biological Tear Fluids; Angewandte Chemie International Edition; 2022
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

Hose pressure transducer by HiTec Zang
Contactless pressure measurement for sterile applications
Easy-to-install tubing pressure sensors for diameters from 4.8-19.1 mm

FireSting-PRO by PyroScience
New fiber optic measuring device: Precise measurements even in the smallest volumes
Measure pH, oxygen and temperature even under sterile conditions

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!

Topic World Spectroscopy
Investigation with spectroscopy gives us unique insights into the composition and structure of materials. From UV-Vis spectroscopy to infrared and Raman spectroscopy to fluorescence and atomic absorption spectroscopy, spectroscopy offers us a wide range of analytical techniques to precisely characterize substances. Immerse yourself in the fascinating world of spectroscopy!
Topic world Diagnostics
Diagnostics is at the heart of modern medicine and forms a crucial interface between research and patient care in the biotech and pharmaceutical industries. It not only enables early detection and monitoring of disease, but also plays a central role in individualized medicine by enabling targeted therapies based on an individual's genetic and molecular signature.

Topic world Diagnostics
Diagnostics is at the heart of modern medicine and forms a crucial interface between research and patient care in the biotech and pharmaceutical industries. It not only enables early detection and monitoring of disease, but also plays a central role in individualized medicine by enabling targeted therapies based on an individual's genetic and molecular signature.


















































