Intestinal stress influences chromosome inheritance
Intestinal cells check the quality of oocytes and intervene when they detect defects
Inheriting a normal and intact number of chromosomes in germ cells, egg and sperm, is essential for the preservation of all species. With increasing age, the risk of the egg cell not inheriting the normal set of chromosomes increases. This results in so-called aneuploidy, which can mean either too many or too few chromosomes. The best-known example is trisomy, also known as Down syndrome in humans. Researchers at the Institute for Genome Stability in Aging and Disease, part of the CECAD Cluster of Excellence for Aging Research at the University of Cologne, have now uncovered that signals from intestinal cells significantly influence the decision whether damaged eggs are eliminated or not in the nematode C. elegans.
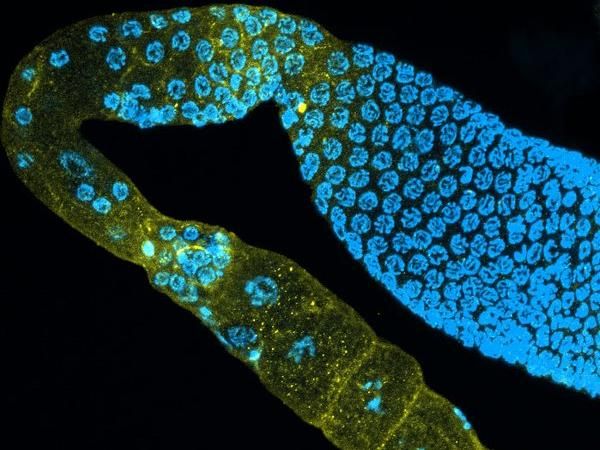
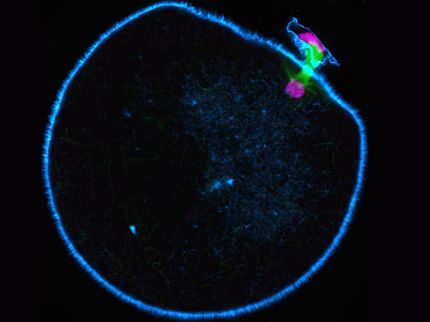
The signalling molecule SYSM-1 (yellow) in the germ cells (blue nuclei) where it regulates the germ cell death.
Siyao Wang
The two scientists Dr Najmeh Soltanmohammadi and Dr Siyao Wang, together with CECAD research group leader Professor Dr Björn Schumacher, investigated the stability of genomes in oocytes (egg cells) of C. elegans. In the germ line, the stability of the chromosomes of the oocytes is closely examined; only intact oocytes survive to be consequently fertilized. The research team now found that responses to environmental stress in the gut lead to the release of a messenger substance that regulates the animal's germline. If control by the stress responses in the gut is absent, egg quality control fails. Despite damaged chromosomes, oocytes survive, more offspring with defective chromosome number are produced, and aneuploidy occurs. The stress response in the intestine reacts both to chromosome damage in the oocytes and to environmental influences such as increased temperatures.
In humans, the quality of the chromosomes in the oocytes is also closely monitored, and in the event of damage, the same mechanisms of cell death occur as in the oocytes of the nematode. With increasing age, the quality of human oocytes decreases. Environmental influences also play an important role in humans, but how they affect egg quality control is still poorly understood. ‘This is precisely why the new findings on the control of oocyte quality in the simple nematode are of such outstanding importance,’ said Schumacher. ‘We have now shown for the first time how stress responses in the gut control the stability of oocyte chromosomes. Understanding how environmental factors control oocyte quality through such stress responses opens up entirely new possibilities to eliminate harmful influences and prevent malformations.’
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.