Deadly spider venom as a basic ingredient of medical applications?
Mystery of the Black Widow decoded
The black widow snatches its prey with venom. The bite of the spider can also be fatal for humans. Until now, it was unclear how the neurotoxin is structured exactly and how it works in detail. The research groups of Professor Richard Wagner, biophysicist at Jacobs University Bremen, and Professor Christos Gatsogiannis from the Institute of Medical Physics and Biophysics at the Westphalian Wilhelms University Münster, have now deciphered the structure and function of the toxin – also with a view to possible medical applications.

Symbolic image
pixabay.com
The black widow uses latrotoxins (LaTXs), a subgroup of neurotoxins, to immobilize or kill its victims. The toxins dock onto specific receptors on the surface of nerve cells and ultimately cause the release of neurotransmitters. Due to the constant influx of calcium ions into the cell, messenger substances are released in large quantities. The result is convulsions.
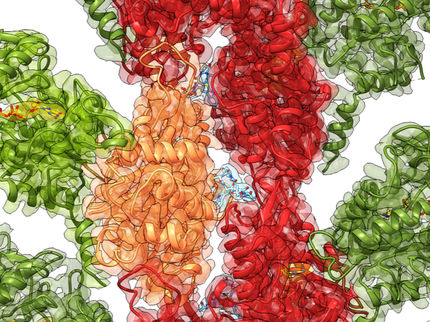
This mechanism distinguishes the latrotoxins from all other variants of the pore-forming toxins. Despite extensive studies over the past decades, it was unclear how these toxins are structured and by which mechanisms they exert their effects. Thanks to cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) in the research group of Professor Gatsogiannis, this has changed. With this three-dimensional method, biomolecules can be "photographed" down to atomic resolution.
In the process, the protein complexes are frozen in liquid ethane at minus 196 degrees Celsius in milliseconds into a thin layer of amorphous ice, a form of solid water. Hundreds of thousands of images are then recorded, showing different views of the protein – and thus revealing the structure of the nerve agent. In addition, Professor Wagner's research group succeeded in clarifying the principle molecular mechanisms of action of latrotoxins in detail with the help of single-molecule electrophysiology (BLM technique). There are only a few laboratories worldwide with the know-how for this method.
Using these two techniques – the cryo-EM and BLM techniques – the researchers, with the participation of the Max Planck Institute in Dortmund, succeeded in elucidating the first structure of a latrotoxin and characterizing its physiological mechanisms of action. It was shown that the spider toxin also spontaneously inserts itself into the cell surface, where it forms highly selective calcium-release ion channels. "The general structure of LaTX is unique and differs from all previously known toxins in every way," Gatsogiannis said.
The new findings are fundamental for understanding the molecular mechanism of action of the entire LaTX family and prepare the ground for possible medical applications as well as for the development of an efficient antidote. In addition, research on insect-specific toxins could open up new possibilities for pest control.
Original publication

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.