Recurrent lockdowns are not necessary for pandemic control
Test-trace-and-isolate has been proven very effective for breaking infection chains
Advertisement
A new study in Science Advances analyses the mitigation of infectious disease outbreaks. It shows that recurrent strict lockdowns are not necessary for long-term control of pandemics – as long as moderate precautionary measures are sustained. The researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization (MPIDS) investigated which measures are required under which conditions to avoid strict lockdowns. They conclude that individual behavior ultimately determines if pandemic control can be maintained.
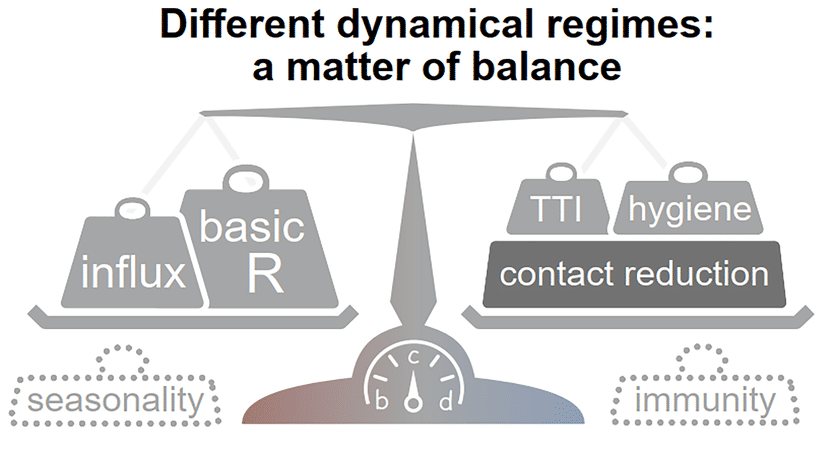
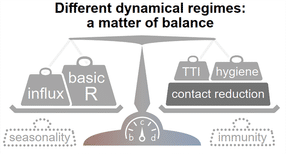
Figure 1: Stability at low case numbers: a matter of balance. Spreading dynamics depend on the balance between destabilizing and stabilizing contributions and on the level of case numbers. Among the factors that destabilize the spread, are the natural contagiousness of the disease and the external influx of infections and possibly seasonality. On the other hand, these factors are counterweighted by increased hygiene, testing strategies, contact reduction and immunity which contribute to stability.
© MPIDS / Priesemann
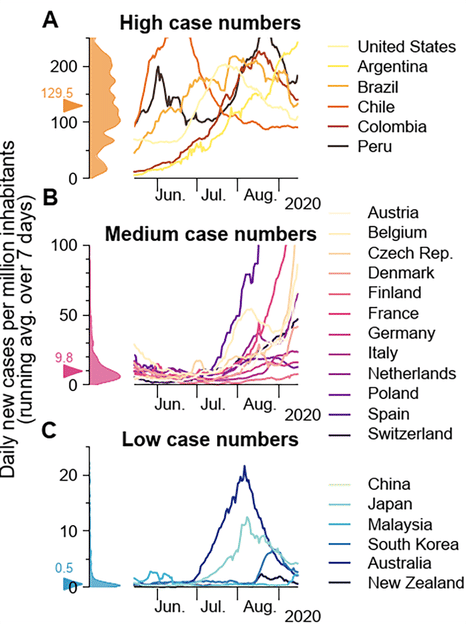
Figure 2: Examples of balance and unbalance based on historic infection data. Strategies of countries to fight SARS-CoV-2 differ widely and are reflected in case numbers. (A) Strategies that involve few non-pharmaceutical interventions rely on the population to hinder the spread in a self-regulated manner and are often accompanied by high case numbers. (B) Strategies that aim to keep case numbers low through extensive test-trace-isolate-strategies, combined with temporary lockdowns, can lead to medium case numbers. As the effectiveness of such strategies depends on daily infections, case numbers can seemingly explode when the (variable) testing capacity limit is exceeded. Many European countries managed to stabilize case numbers over summer 2020. However, with seasonality in autumn, and influx of new cases from abroad, the pandemic tipped over to instability, and they quickly saw case numbers rising faster than exponentially. (C) When the external influx is low or strategies used to reduce contacts are very effective, the stable regime can be reached. In this case, average case numbers are very low, and local outbreaks can be controlled well through local interventions. (Mind the different y-axes!) Raw data and preliminary visualizations were obtained from https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus
© MPIDS / Priesemann
Together with his colleagues, Sebastian Contreras from the MPIDS studied the control of disease spread via so-called non-pharmaceutical interventions. Those include mandatory governmental measures and voluntary actions, such as physical distancing, everyday habits, and face masks. The scientists found a stable regime at low case numbers, where freedom is maximized without the need for recurrent lockdowns. Yet, a critical factor in maintaining this freedom is the continuation of a fast and efficient 'test-trace-and-isolate' system.
Test-trace-and-isolate has been proven very effective for breaking infection chains
During the COVID-19 pandemic, test-trace-and-isolate strongly contributed to contain disease spread; by following the close contacts of infected individuals, infection chains can be broken. However, this approach can only be effective if it is timely and when case numbers are within the finite tracing capacity of health authorities. The researchers found that testing and contact tracing can stabilize COVID-19 incidence at low values while requiring fewer measures to protect the population's health. Yet, this stability is conditional to the measures in place (both voluntary and governmental) and the contact tracing capacity of health authorities; it is a matter of balance (as illustrated in Figure 1).
"Making an analogy, the test-trace-and-isolate system that can stop infection chains in COVID-19 resembles firefighters who can stop wildfires. In both cases, it is much easier to contain the outbreaks locally while it is still small. Once the outbreak got out of control, the test-trace-isolate becomes too slow and unspecific; one has to reinstate strong population-scale measures and, in parallel, try to protect the vulnerable," says Viola Priesemann, who coordinated the study. "Vaccination and other voluntary measures to prevent contagion will further facilitate control, acting as a very convenient rain in our analogy of fire," Sebastian Contreras adds.
The model reflects the pandemic development in the recent past
Besides the new mathematical evidence presented by the researchers, there are real-world examples of their findings following the winter COVID-19 wave in 2020 (shown in Figure 2). Nonetheless, the results are general and apply to arbitrary infectious diseases, not restricted only to the COVID-19 pandemic. Therefore, they will allow policymakers to plan effective response strategies in the future. As the next step in their research, the authors aim to analyze the factors behind adherence and compliance to the measures by studying the interplay between disease and information spread.