Optimal concentrations of enzymes and their substrates
Until now, scientists assumed that no general relationship exists between the individual concentrations
Biological cells invest much of their resources into the production of enzymes, which catalyze the conversion of substrates into products. An international team of bioinformaticians and biophysicists, led by Prof. Martin Lercher from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU), discovered that these processes are most efficient at a certain relationship between the intracellular enzyme and substrate concentrations. They describe this discovery in the current issue of the journal PLOS Biology.
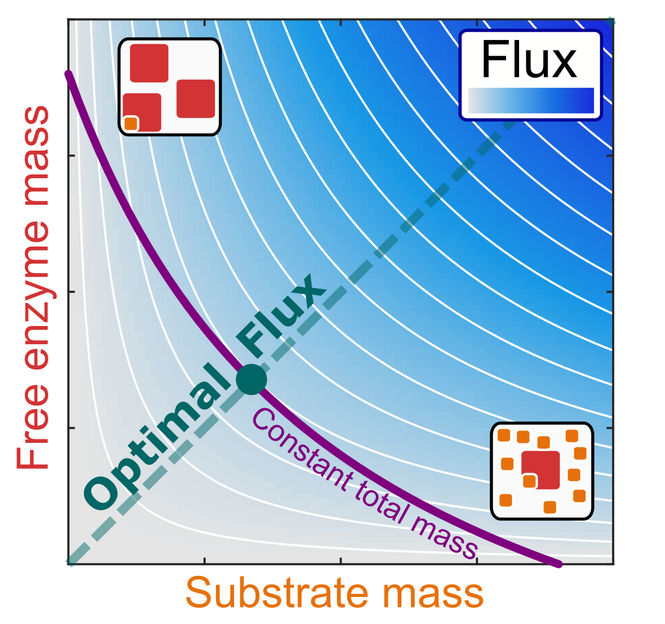
Schematic representation of the relationship between reaction flux (blue shading) and the mass concentrations of an enzyme and its substrate, with optimal efficiency along the diagonal.
HHU / Martin Lercher
Without enzymes, biological cells cannot function. Enzymes catalyze countless chemical reactions that would otherwise run too slowly or not at all. Thus, enzymes are essential molecular tools of cells to produce their building blocks, but also to regulate their processes.
Biological cells contain hundreds of different enzyme and substrate types. For molecular biology and for many areas of medicine, it is important to understand how their concentrations affect cellular functions. Such knowledge also helps biotechnologists to develop more efficient biological factories based on enzymes.
Until now, scientists assumed that no general relationship exists between the individual concentrations. A team of researchers of the HHU Institute for Computational Cell Biology and the Department of Physics of the University of California, San Diego (UCSD), has now derived such a relationship, based on the consideration of processes with optimal cellular efficiency.
The researchers conclude that the intracellular mass of a substrate should be equal to the mass of the free enzymes that are waiting to convert it into products. This relationship was confirmed with experimental data for the bacterium E. coli.
Prof. Lercher said about their results: „It is amazing that such a simple relationship seems to govern the concentrations in living cells. I wouldn’t be surprised if this important result will eventually find its way into textbooks for biochemistry and cellular physiology.”
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.




















































