A tiny molecule with a big impact
Immunologists have deciphered a new role of nitric oxide in the defense against pathogens.
Nitric oxide (NO) occurs naturally in the human body as a messenger substance. It is considered an all-rounder, as it performs numerous important regulatory functions, including immune defense against pathogens. The exact mode of action of this molecule has now been uncovered by immunologist Prof. Dr. Andreas Müller from the Institute of Molecular and Clinical Immunology at the University Medical Center Magdeburg together with scientists from the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research Braunschweig. The findings are crucial for the development of new therapeutic approaches for the treatment of infectious diseases, but also of diseases caused by excessive inflammation. The results were published in the journal "Immunity".
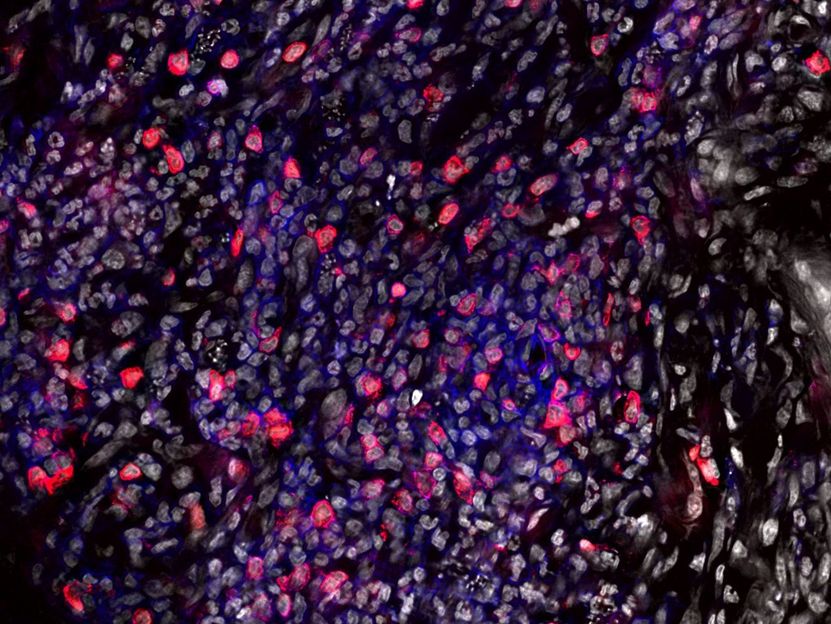
Microscopy image of a Leishmania major infection site in the skin. T cells (red) and phagocytes (blue) work together to fight the pathogen, but Leishmania major also uses phagocytes as a habitat. The nuclei of the immune cells recruited to the infection site are stained white, and the pathogens can be seen as small white dots.
IMKI Magdeburg
Prof. Müller explains: "NO has two very different effects during an infection: On the one hand, it can directly destroy pathogens that have been taken up by phagocytes. On the other hand, above a certain concentration, NO prevents the recruitment of further phagocytes to the site of infection, thus preventing unnecessary tissue damage that would be caused by an excessive immune response." Using the example of Leishmania major, the causative agent of a tropical disease that has so far been difficult to treat, the research group measured and modeled the two modes of action of NO over the entire course of an immune response.
The scientists were able to show that the direct destruction of the pathogen by NO is the most important defense mechanism of the immune system against Leishmania major during a relatively short period of time. "Instead, NO is much more effective at preventing the phagocytes in which Leishmania major can proliferate from reaching the site of infection. Because NO inhibits the recruitment of these phagocytes, it deprives the pathogen of the basis for multiplication," explains Prof. Müller, the study's final author.
For their experiments, the scientists have developed their own measuring system in order to be able to determine the growth rate and viability of the pathogens during infection. "Using so-called intravital 2-photon microscopy, we were able to observe the pathogens in living tissue during infection and measure their proliferation or destruction by the immune system. The data thus obtained were used to test the predictions of mathematical models we had made of how the immune system works, and these predictions matched our data exactly." With this better understanding of the interplay between the various mechanisms of immune defense, he said, it is now possible to intervene specifically in the regulation of the immune system and thus develop new treatment approaches in the fight against infectious diseases.
Original publication
Original publication
"Nitric oxide controls proliferation of Leishmania major by inhibiting the recruitment of permissive host cells"; Immunity; 2021
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.