Protein distancing
Researchers have developed a new method to attach proteins to the surface of virus-like particles
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI are the first to have joined two proteins together by means of a free-standing, rigid link. The structural element holds the two protein molecules together at a defined distance and angle, much the way a barbell handle connects two weights. This type of linkage could help, for example, to develop so-called virus-like particles for vaccines. The researchers report their results in the journal Structure.
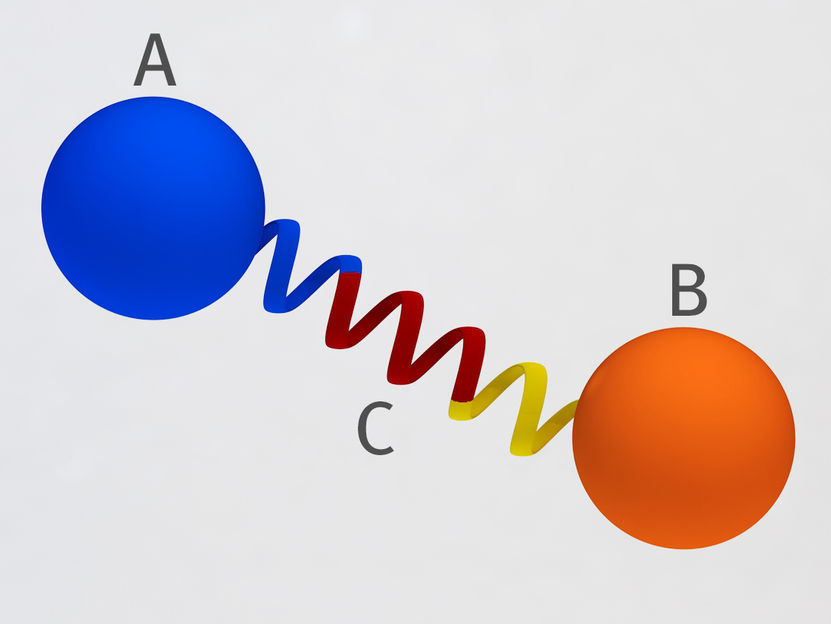
Principle of the protein bridge developed at PSI: Two proteins (A and B) are connected to each other at a fixed distance and angle by means of a rigid protein spiral (C). Thus they cannot come near each other and cannot interact.
Mahir Dzambegovic, Paul Scherrer Institut
"Proteins have been optimised in evolution over millions of years," says molecular biologist Roger Benoit from the PSI Laboratory for Nanoscale Biology. "In nature, where proteins need to be rigid, they are. But it's difficult to mimic that in the laboratory."
If you want to join two proteins yet hold them at a defined distance and angle via a protein bridge, you're in for a hard time. The connecting element usually turns out to be too flexible, allowing the two proteins to come too close to each other. It is as if you were to bind two weights together with a rope. As soon as you lift the rope so the weights can swing freely, they come together. When protein molecules approach each other, though, they can interact. Contacts between the proteins often restrict the natural freedom of movement in the structure – the molecules move differently than they would if there were no contact with the other protein.
There could be many applications for bonds with lower flexibility, yet designing them is difficult. "Often, it is hard to predict the way the proteins fold and what their structure looks like in reality," Benoit says. That is, stringing several proteins together with the desired spacing and orientation usually requires extremely complex optimisation in the laboratory.
Roger Benoit and his team have now found a solution. They used a segment of a protein that plays a role, for example, in wound healing in the human body. Part of this protein forms a helix, a spiral form. Its backbone is stabilised by interactions between its side chains. Thus, the helix remains intact on its own and is quite rigid – almost like a metal spiral made of hardened steel. With this Benoit successfully linked several proteins to one another in the desired manner.
In terms of the barbell analogy, that means the researchers now have bound the proteins together using a spiral of metal instead of a rope, thus keeping the distance between them constant. This way, they also set the two proteins' orientation to each other.
Input for new vaccines
Such rigid connections have the potential for many practical applications. Among other things, they could prove helpful in the development of vaccines against viruses, including Sars-CoV-2.
Vaccines are often produced by making the pathogens inactive. They can no longer harm humans, but they stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies. Virus-like particles prepared in the laboratory are another option. Many surface proteins characteristic of a virus are attached to the surfaces of these virus-like particles, so that the immune system detects them and then generates antibodies.
One advantage offered by virus-like particles is that, because they contain none of the pathogen's genetic material, there is no chance they will multiply. For this reason, they are safer than weakened pathogens, and they are currently under investigation for protection against several viruses, such as the hepatitis B and human papilloma viruses.
With the rigid connector, virus proteins could be attached to the surface of such virus-like particles more precisely. The limited flexibility of the helix offers advantages: "If the connection between the particle and the virus protein is too flexible, the proteins could possibly fold back again, and then they are no longer accessible," Benoit explains. The immune system doesn't recognise them as well. If the proteins stand out more from the particles and all present themselves at a predetermined angle and distance, as is possible with the spacer, better and more effective vaccines could be developed.
Bones and silk
Benoit hopes that new biomaterials can also be created in this way. The helix could serve as a building block in combination with other proteins. In the future, researchers may be able to build 3D protein scaffolds, for example, to replace a piece of bone. "Or you could use it to combine proteins into long strings and create new silk-like textiles, which then could even be biodegradable."
Researchers at PSI and research institutes worldwide who are working on the structural elucidation of proteins should also benefit from the new method. That's because protein molecules linked via the rigid helix could be optimised so that they crystallise and yet retain their natural freedom of movement in the crystals. This would make it easier to examine their structure. With new methods of protein crystal structural analysis, for example using the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL at PSI, proteins can even be observed in action, for example when membrane pumps transport substances out of a cell.