Flowers of St. John's Wort serve as green catalyst
Conceptually new and sustainable process registered as a German patent
An interdisciplinary team of scientists from the School of Science at TU Dresden has for the first time used dried flowers of St. John's Wort (genus Hypericum) as an active catalyst in various photochemical reactions. This conceptually new and sustainable process was registered as a German patent and presented in the journal “Green Chemistry”.
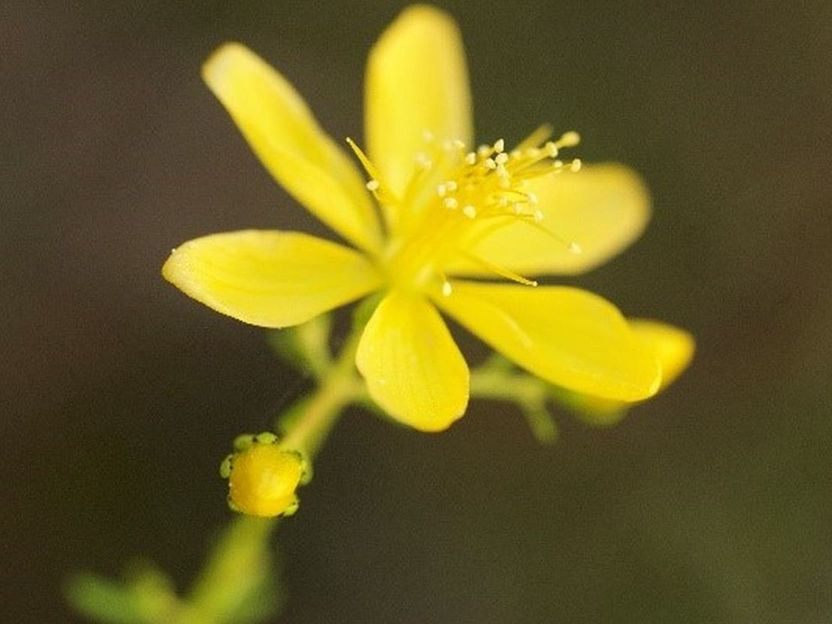

The flowers of St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum) have not only healing but also catalytic effects.
Julia Naumann
Since ancient times, St. John's Wort has been used as a medicinal herb covering a wide range of applications such as the treatment of burns, skin injuries, neuralgia, fibrosis, sciatica and depression. Due to its high medicinal potential, the plant known in technical terminology as Hypericum perforatum even became "Medicinal Plant of the Year" in 2015. Now, scientists at TU Dresden have shown that there is much more to the herb than its healing properties.
To this end, two interdisciplinary groups from biology and inorganic chemistry have joined forces and thus achieved astonishing results. Originally, the research groups led by botanist Prof. Stefan Wanke and chemist Prof. Jan. J. Weigand wanted to synthesize graphene-like 2D structures from natural products in the joint project funded by the Sächsische Aufbaubank. For this purpose, hypericin, a compound of St. John's Wort, served as a template and starting material. In the course of the investigations, it turned out that hypericin efficiently catalyzes photochemical reactions. Prof. Weigand then came up with the idea of using the dried flowers of St. John's Wort, from which hypericin can be obtained by extraction, as a green and sustainable alternative to common catalysts.
"The chemistry of natural substances and especially the background of botany were completely new to us. The exciting results that came out of it are all the more gratifying. The interdisciplinary project shows how important it is in science to think outside the "box,"" says Prof. Weigand, commenting on the success of the collaboration.
The team is thus following a current trend in modern synthetic chemistry to include sustainable aspects. The search for sustainable, renewable and environmentally friendly photoredox catalysts is proving to be extremely challenging. The results now obtained are all the more promising. The plant compound hypericin, a secondary metabolite from St. John's Wort, is used as the active compound in chemical reactions without the need for prior chemical processing. The Dresden scientists have successfully applied for a German patent for this newly developed method (DE 10 2019 215 871).
Also Prof. Wanke is amazed at the success of the collaboration: "Although the research project started with a good idea, bringing it to life was not entirely trivial, as the two working groups first had to "get to know" each other. Our research fields and methods used were far apart. But soon the first unusually exciting results emerged. Everyone involved learned a lot. We would like to continue the research, but the funding is still missing.”
Original publication
Original publication
Jun-jie Wang, Kai Schwedtmann, Kun Liu, Stephen Schulz, Jan Haberstroh, Gerrit Schaper, Anja Wenke, Julia Naumann, Torsten Wenke, Stefan Wanke und Jan J. Weigand; "Flowers of the plant genus Hypericum as versatile photoredox catalysts"; Green Chem.; 2021,23, 881-888.
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents

Orikine Bio secures €800k in innovation research funding to advance groundbreaking autoimmune disease therapy - Orikine Bio’s technology platform is on the cusp of revolutionizing the future of immunotherapy

A free AI tool to quickly determine which protein labeling strategy works best for molecular interaction measurements - NanoTemper Technologies and PharmAI launch Proto
Novel method for fast 3D microscopy
Researchers identify food products that could reduce COVID transmission - The products can reduce the transmission potential of airborne pathogens by thickening and reducing a person’s saliva



















































