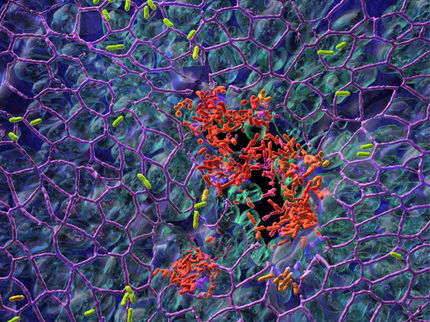
Nanocrystals that eradicate bacteria biofilm
Research team finds ways to control the surface texture of nanostructures
The COVID-19 pandemic is raising fears of new pathogens such as new viruses or drug-resistant bacteria. To this, a Korean research team has recently drawn attention for developing the technology for removing antibiotic-resistant bacteria by controlling the surface texture of nanomaterials.
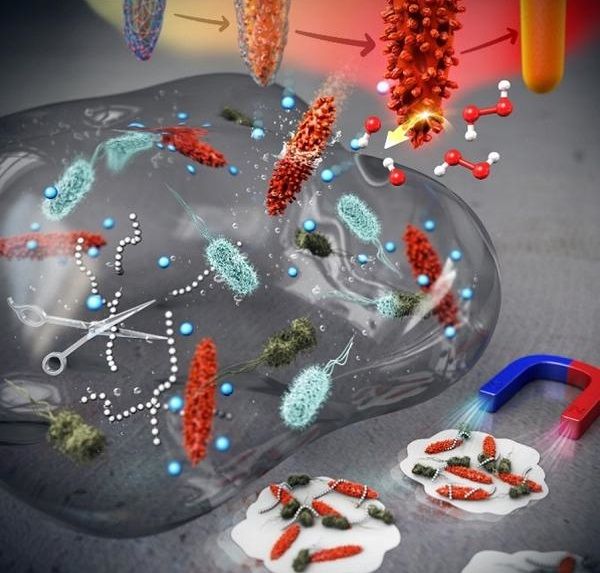
Schematic diagram showing removal of bacterial biofilm via Mtex
POSTECH
A joint research team from POSTECH and UNIST has introduced mixed-FeCo-oxide-based surface-textured nanostructures (MTex) as highly efficient magneto-catalytic platform in the international journal Nano Letters. The team consisted of professors In Su Lee and Amit Kumar with Dr. Nitee Kumari of POSTECH's Department of Chemistry and Professor Yoon-Kyung Cho and Dr. Sumit Kumar of UNIST's Department of Biomedical Engineering.
First, the researchers synthesized smooth surface nanocrystals in which various metal ions were wrapped in an organic polymer shell and heated them at a very high temperature. While annealing the polymer shell, a high-temperature solid-state chemical reaction induced mixing of other metal ions on the nanocrystal surface, creating a number of few-nm-sized branches and holes on it. This unique surface texture was found to catalyze a chemical reaction that produced reactive oxygen species (ROS) that kills the bacteria. It was also confirmed to be highly magnetic and easily attracted toward the external magnetic field. The team had discovered a synthetic strategy for converting normal nanocrystals without surface features into highly functional mixed-metal-oxide nanocrystals.
The research team named this surface topography - with branches and holes that resembles that of a ploughed field - "MTex." This unique surface texture has been verified to increase the mobility of nanoparticles to allow efficient penetration into biofilm matrix while showing high activity in generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) that are lethal to bacteria.
This system produces ROS over a broad pH range and can effectively diffuse into the biofilm and kill the embedded bacteria resistant to antibiotics. And since the nanostructures are magnetic, biofilm debris can be scraped out even from the hard-to-reach microchannels.
"This newly developed MTex shows high catalytic activity, distinct from the stable smooth-surface of the conventional spinel forms," explained Dr. Amit Kumar, one of the corresponding authors of the paper. "This characteristic is very useful in infiltrating biofilms even in small spaces and is effective in killing the bacteria and removing biofilms."
"This research allows to regulate the surface nanotexturization, which opens up possibilities to augment and control the exposure of active sites," remarked Professor In Su Lee who led the research. "We anticipate the nanoscale-textured surfaces to contribute significantly in developing a broad array of new enzyme-like properties at the nano-bio interface."
Original publication
Most read news
Original publication
Nitee Kumari, Sumit Kumar, Mamata Karmacharya, Sateesh Dubbu, Taewan Kwon, Varsha Singh, Keun Hwa Chae, Amit Kumar*, Yoon-Kyoung Cho*, and In Su Lee*; "Surface-Textured Mixed-Metal-Oxide Nanocrystals as Efficient Catalysts for ROS Production and Biofilm Eradication"; Nano Lett.; 2020
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.