Detecting COVID-19 antibodies in 10-12 seconds
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University report findings on an advanced nanomaterial-based biosensing platform that detects, within seconds, antibodies specific to SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for the Covid-19 pandemic. In addition to testing, the platform will help to quantify patient immunological response to the new vaccines with precision.
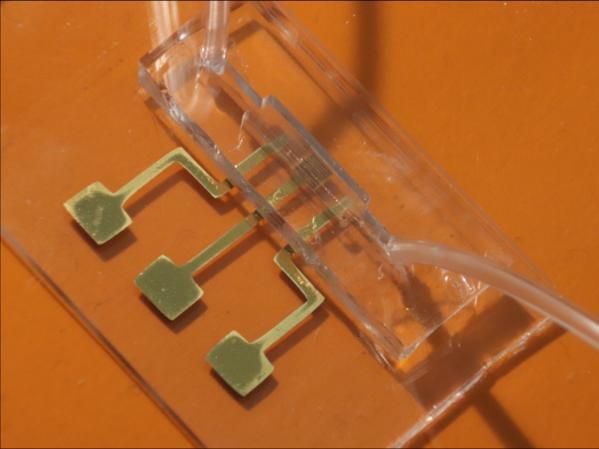
An image of the COVID-19 test chip made by aerosol jet nanoparticle 3D printing.
Advanced Manufacturing and Materials Lab, College of Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University
The results were published in the journal Advanced Materials. Carnegie Mellon's collaborators included the University of Pittsburgh (Pitt) and the UPMC.
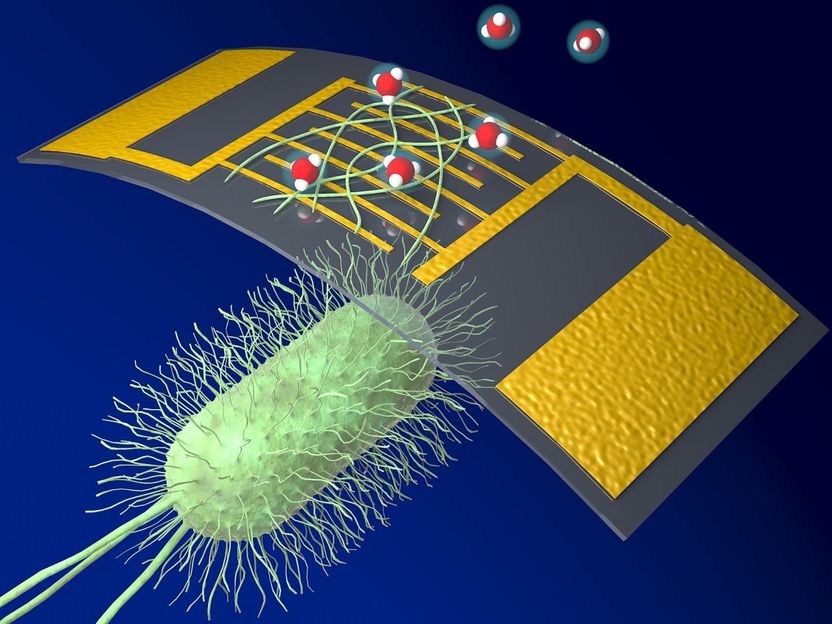
The testing platform identifies the presence of two of the virus' antibodies, spike S1 protein and receptor binding domain (RBD), in a very small drop of blood (about 5 microliters). Antibody concentrations can be extremely low and still detected below one picomolar (0.15 nanograms per milliliter). This detection happens through an electrochemical reaction within a handheld microfluidic device which sends results almost immediately to a simple interface on a smart phone.
"We utilized the latest advances in materials and manufacturing such as nanoparticle 3D printing to create a device that rapidly detects COVID-19 antibodies," said Rahul Panat, an associate professor of mechanical engineering at Carnegie Mellon who uses specialized additive manufacturing techniques for research ranging from brain-computer interfaces to biomonitoring devices.
An additive manufacturing technology called aerosol jet 3D printing is responsible for the efficiency and accuracy of the testing platform. Tiny, inexpensive gold micropillar electrodes are printed at nanoscale using aerosol droplets that are thermally sintered together. This causes a rough, irregular surface that provides increased surface area of the micropillars and an enhanced electrochemical reaction, where antibodies can latch on to antigens coated on the electrode. The specific geometry allows the micropillars to load more proteins for detection, resulting in very accurate, quick results.
The test has a very low error rate because the binding reaction between the antibody and antigen used in the device is highly selective. The researchers were able to exploit this natural design to their advantage.
The results come at an urgent time during the COVID-19 pandemic. "Because our technique can quantify the immune response to vaccination, it is very relevant in the current environment," Panat said.
Panat collaborated with Shou-Jiang Gao, leader of the cancer virology program at UPMC's Hillman Cancer Center and professor of microbiology and molecular genetics at Pitt. Azahar Ali, a researcher in Panat's Advanced Manufacturing and Materials Lab, was the lead author of the study.
Rapid diagnosis for the treatment and prevention of communicable diseases is a public health issue that goes beyond the current COVID-19 pandemic. Because the proposed sensing platform is generic, it can be used for the rapid detection of biomarkers for other infectious agents such as Ebola, HIV, and Zika. Such a quick and effective test could be a game-changer for controlling the spread of diseases.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous

Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous