Proteomic profiling reveals innovation potential of new antibiotics
Research team intends to use proteomics to accelerate the development of new drugs
Advertisement
The fight against bacterial infections, especially those caused by resistant pathogens, is in full swing with the search for new antibiotic agents. The aim is to identify substances that attack the pathogens in a truly novel way. The team at the Center for Systems-Based Antibiotic Research (Cesar) at Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) has described in two publications how assess if a new antibiotic has a new mechanism of action. They analysed the proteome, i.e. the totality of all proteins present in the bacterium, to learn how the cell reacts to stress. The team published their findings in the journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy posted as accepted article on 12 October 2020. In another paper in the journal proteomics accessible online as early view since 19 September 2020, the team evaluated the applicability of a method for determining the molecular target of antibiotics.
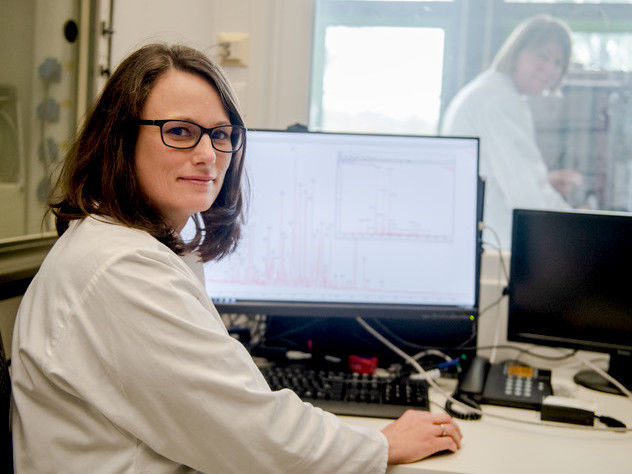

Dr. Sina Schäkermann is lead author of one of the two reports published on the proteome-based search for new antibiotically active substances.
© RUB, Marquard
How a bacterium reacts to almost 100 substances
The researchers, including many RUB students, over many years have been studying changes in the proteome of the model organism Bacillus subtilis after exposure to various drugs. “The current study is a compilation of the responses to almost 100 substances,” explains Professor Julia Bandow, Chair of Applied Microbiology and Head of Cesar.
The bacterium’s response to antibiotic treatment mirrors the physiological stress, so to speak: for example, if the antibiotic causes a disruption of the fatty acid biosynthesis pathway, the enzymes in that pathway are upregulated. “Since it is quite well understood how Bacillus subtilis adapts to changing conditions and how the bacterium reacts to different stress factors, we often can use the proteome response to draw conclusions about which process in the cell is impaired by a new antibiotic,” Julia Bandow explains the comparison of proteomic responses approach, CoPR for short.
Similar or new mechanism of action
This provides a basis for determining whether a promising new antibiotic substance has a similar effect to already known ones or whether it does indeed have a new mechanism of action. “We are always happy to see a new proteome response, because this indicates that the substance acts differently than the antibiotics previously tested,” explains the researcher. In that case, she says, the proteome is then analysed in great detail to build hypotheses on the cause of the response and thus the mechanism of action.
As examples, the researchers examined more closely salvarsan, the first antibiotic ever used in humans, the antibiotic anti-rheumatic auranofin, a new atypical tetracycline, and the new class of trans-translation inhibitors.
Which protein is the target?
For new antibiotics with innovative mechanisms of action, the next essential step is to elucidate the direct molecular target in the bacterial cell. To this end, the second study explored the applicability of a technique for target identification developed in Andrew Emili’s group (Boston University) to antibiotic research. It is based on chromatographic co-elution of active ingredient and target protein. The researchers incubated the proteins from bacterial cells with the antibiowtic allowing it to bind to its target. In the next step, the proteins were separated by chromatography. When the active ingredient tightly binds to the target protein, it travels with it during the separation process.
The research team then used mass spectrometry to search for the antibiotic. In addition to the target-bound antibiotic, excess free antibiotic can also be found. “When the active substance is subjected to the same chromatographic separation without proteins, it is possible to determine which of the fractions contain the free active substance. The other fractions are then those containing the target protein,” says Julia Bandow.
In their study, the Cesar team not only confirmed the site of action of a widely studied antibiotic, but also clarified that this technique can be used to detect many potential antibiotic targets. “This confirms the potential of this method for identifying new targets,” concludes Bandow.
Original publication
Christoph H. R. Senges, Jennifer J. Stepanek et al.; "Comparison of proteomic responses as global approach to antibiotic mechanism of action elucidation"; Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; 2020.
Sina Schäkermann, Dominik Wüllner, Abdulkadir Yayci, Andrew Emili, Julia Elisabeth Bandow; "Applicability of chromatographic co-elution for antibiotic target identification"; Proteomics; 2020.