How to map brain connections using DNA barcodes
A new method developed at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) uses DNA sequencing to efficiently map long-range connections between different regions of the brain. The approach dramatically reduces the cost of mapping brain-wide connections compared to traditional microscopy-based methods.
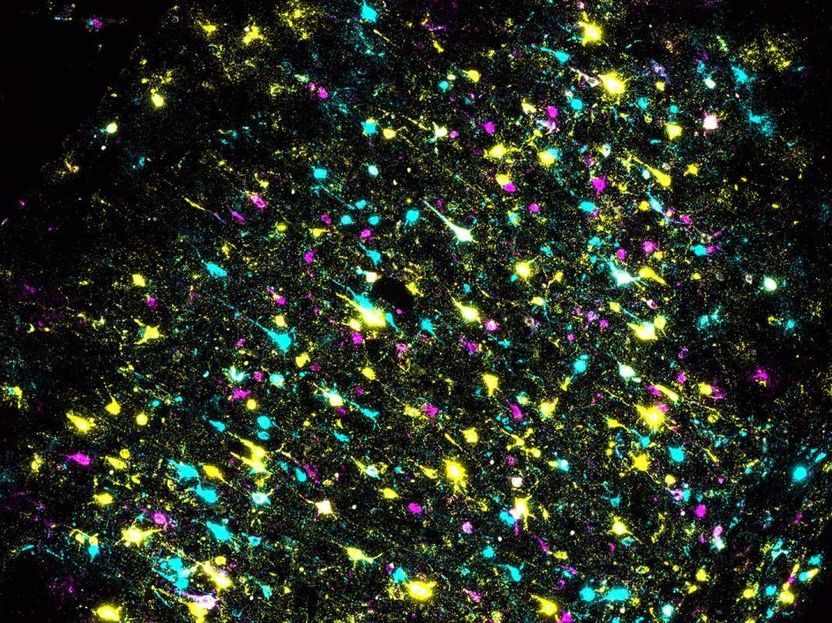
A section of mouse brain stained to identify individual neurons and all their connections. Each color represents a different DNA barcode.
Xiaoyin Chen, Zador lab/CSHL
Neuroscientists need anatomical maps to understand how information flows from one region of the brain to another. "Charting the cellular connections between different parts of the brain--the connectome--can help reveal how the nervous system processes information, as well as how faulty wiring contributes to mental illness and other disorders," says Longwen Huang, a postdoctoral researcher in CSHL Professor Anthony Zador's lab. Creating these maps has been expensive and time-consuming, demanding massive efforts that are out of reach for most research teams.
Researchers usually follow neurons' paths using fluorescent labels, which can highlight how individual cells branch through a tangled neural network to find and connect with their targets. But, the palette of fluorescent labels suitable for this work is limited. Researchers can inject different colored dyes into two or three parts of the brain, then trace the connections emanating from those regions. They can repeat this process, targeting new regions, to visualize additional connections. In order to generate a brain-wide map, this must be done hundreds of times, using new research animals each time.
The method developed in the Zador lab, called brain-wide individual animal connectome sequencing (BRICseq), takes a different approach. "We no longer label brain regions and their projections using colors. We are labeling them using nucleotide sequences," Huang says. Combining the four letters of the DNA code into short "barcodes" generates a virtually infinite number of labels that can distinguish one cell from one another, he explains. After labeling, researchers use DNA sequencing to analyze tiny segments of brain tissue, interpreting each recurring barcode as a signal of a cellular connection.
"The diversity of barcodes is really high compared to the number of colors we can use in science research. So now we can really label a huge amount of neurons and brain regions per animal, which allows us to map projections from multiple brain regions using these barcodes," Huang says.
The research team, including former graduate student Justus Kebschull, who worked with Huang to develop the technique, report in the journal Cell that BRICseq accurately maps region-to-region connectivity in the brains of mice. They say the approach will be widely accessible and should be adaptable to other organisms.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.