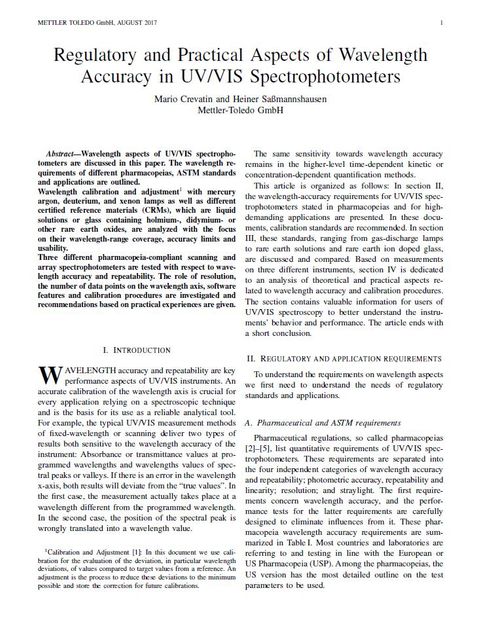
Diagnostic biosensor quickly detects SARS-CoV-2 from nasopharyngeal swabs
New test analyzes patient samples without any sample preparation steps
According to many experts, early diagnosis and management are critical for slowing the spread of SARS-CoV-2, the new coronavirus that causes COVID-19. Therefore, the race is on to develop diagnostic tests for the virus that are faster, easier and more accurate than existing ones. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Nano have developed a field-effect transistor-based biosensor that detects SARS-CoV-2 in nasopharyngeal swabs from patients with COVID-19, in less than one minute.
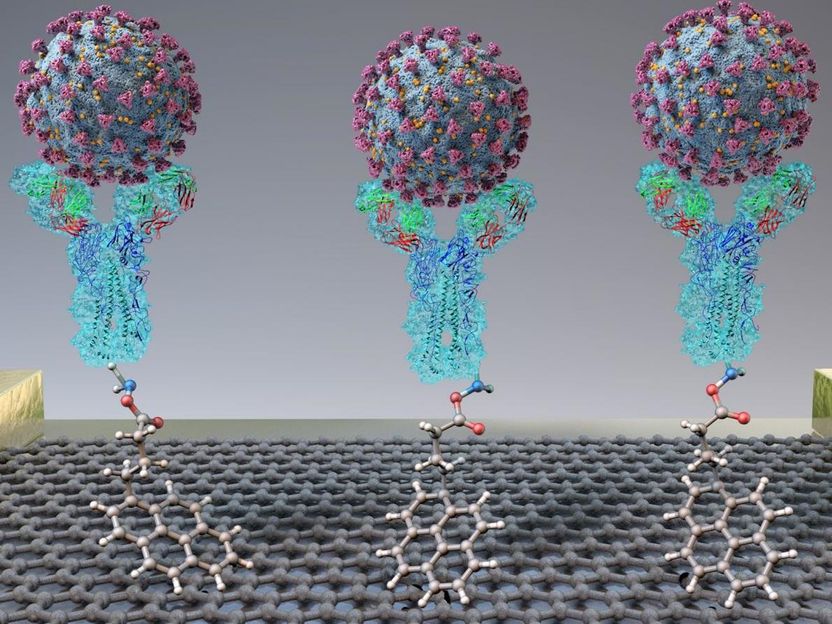
A new test quickly detects SARS-CoV-2 (spheres) through binding to antibodies (Y-shapes) on a field-effect transistor.
Adapted from ACS Nano 2020, DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.0c02823
Currently, most diagnostic tests for COVID-19 rely on a technique called real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), which amplifies SARS-CoV-2 RNA from patient swabs so that tiny amounts of the virus can be detected. However, the method takes at least 3 hours, including a step to prepare the viral RNA for analysis. Edmond Changkyun Park, Seung Il Kim and colleagues wanted to develop a faster diagnostic test that could analyze patient samples directly from a tube of buffer containing the swabs, without any sample preparation steps.
The team based their test on a field-effect transistor -- a sheet of graphene with high electronic conductivity. The researchers attached antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to the graphene. When they added either purified spike protein or cultured SARS-CoV-2 virus to the sensor, binding to the antibody caused a change in the electrical current. Next, the team tested the technique on nasopharyngeal swabs collected from patients with COVID-19 or healthy controls. Without any sample preparation, the sensor could discriminate between samples from sick and healthy patients. The new test was about 2-4 times less sensitive than RT-PCR, but different materials could be explored to improve the signal-to-noise ratio, the researchers say.
Original publication
Other news from the department science
These products might interest you

Octet R2 / Octet R4 / Octet R8 by Sartorius
Full power on 2, 4 or 8 channels: Label-free and GxP-compliant analysis of molecular interactions
Innovative label-free real-time protein quantification, binding kinetics and rapid screenings

Octet SF3 by Sartorius
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) using Single Dynamic Injections for Kinetics and Affinities
Curvature is Key - Adding a ‘Third Dimension’ to the Binding Curve

Octet RH16 and RH96 by Sartorius
Efficient protein analysis for process optimisation and manufacturing control in high-throughput
Label-free protein quantification and characterization of protein-protein interactions

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Survive_AIDS