New method to monitor Alzheimer's proteins
Terahertz waves detect the fibrillization state of amyloid beta proteins in solution
Advertisement
Physicists at the Center for Integrated Nanostructure Physics (CINAP), within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS, South Korea), have reported a new method to identify the aggregation state of amyloid beta (Aβ) proteins in solution. Published in ACS Nano, this finding could represent a step forward in the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease.
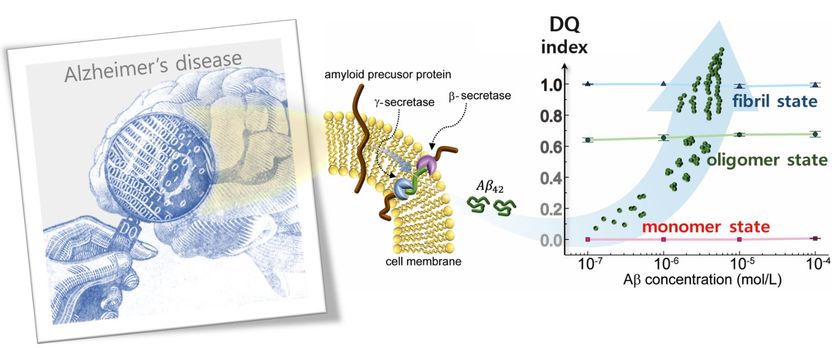
The monomer, oligomer and fibrillar forms of the Aβ protein are distinguished using THz near-field conductance measurements. Independently of the protein concentration, the DQ index goes from zero to one: nearly zero is a monomer state, a value of 0.64 indicates the presence of oligomers, and one corresponds to the more advanced fibril state.
IBS
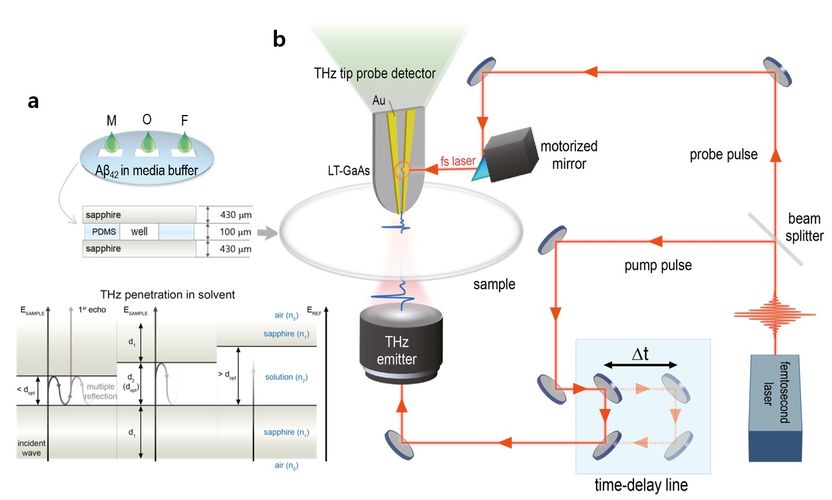
(a) Samples of the Aβ proteins in monomer (M), oligomer (O) and fibril (F) form are analysed inside small wells sandwiched by sapphire plates. With a small amount of sample, it was possible to detect THz signals without noise. (b) Solution-based sample preparation for the THz near-field time-domain spectroscopy system.
IBS
The gradual accumulation of Aβ in the brain leads to incurable dementia. The disease progression is strongly correlated with the form of the Aβ proteins: 4-nm-size monomers evolve to oligomer of several hundred nanometers and reaches the fibrillar state forming plaques of up to a few tens of micrometers in size.
The researchers clearly discerned the different Aβ stages using THz near-field conductance measurements. This technique measures the energy absorbed by molecules at an energy band of around 1-10 meV (or 0.2-2.4 THz), and it is considered an effective technique for investigating the transformation of biological macromolecules without generating heat. The scientists measured how Aβ proteins in the solution are disturbed by incident THz radiation and noticed that the results were correlated with the form of the Aβ proteins: monomer, oligomer and fibril. Then, they derived the optical conductance, which decreases with the evolving fibrillization states and increases with the elevating molar concentrations.
Since the progressive stages of the disease can be differentiated simply with this technique, the team derived a dementia quotient (DQ) from the optical conductance, using the so-called Drude-Smith model. A DQ value of around one indicates that Aβ is in a fibril state, around 0.64 an oligomeric state, and nearly zero is at a monomeric state.
"We believe that our result gives us a significant paradigm shift in the Alzheimer's disease research field, since the dementia quotient is clearly identified from the label-free conductance measurement of different Aβ protein structural states," says Chaejeong Heo, one of the leading authors of this study. CINAP Director, Young Hee Lee adds "This index can be useful for early detection of toxic Aβ protein aggregation and fibrillization observed in Alzheimer's disease."























































