Cellular Identity: How stem cells decide their identity
Advertisement
Several hundred different cell types of the adult human body are formed during embryonic development, starting from just a few identical stem cells. The differentiation potential of the cells is progressively restricted in the course of this process, causing changes in their morphology and functions. A research team headed by Prof. Dr. Sebastian Arnold and Jelena Tosic from the Faculty of Medicine at the University of Freiburg has now succeeded in deciphering basic molecular control mechanisms by which stem cells decide which embryonic cell types to turn into. This is achieved at least partially through selective usage of the genes for each different cell type, despite the presence of the identical genetic information in every cell in the body.
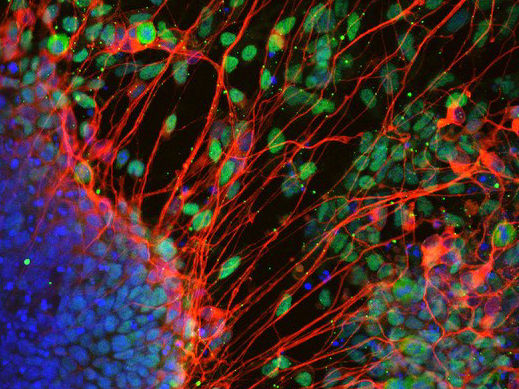
Neurons derived from stem cell in the absence of T-Box factors.
Carsten Schwan/ Jelena Tosic
The undifferentiated stem cells of the embryo develop either into cells of the nervous system, the so-called neuroectoderm, or into cells of the meso- and endoderm, from which, for example, many different cell types of the internal organs or the muscles develop. For over 25 years it has been known that this decision is regulated by embryonic signaling molecules, such as TGFβ and Wnt signals. So far, however, it has remained unclear exactly how these signals control this first decision of cell differentiation. The study, carried out in the context of Tosic's doctoral thesis, shows that the embryonic TGFβ and Wnt signals are transmitted by gene-regulating transcription factors of the T-box factor family, namely Eomes and Brachyury. These factors are responsible for “turning on” the differentiation gene programs for all meso- and endoderm cells. At the same time, these T-box factors also act as gene repressors, preventing the formation of neural tissue by suppressing the corresponding gene programs. This involves changes in the structure but not the content of the genetic information in the cell nucleus.
"The results of the study represent a crucial step towards understanding the basic mechanisms of how cells develop their future identity during development," says Arnold. They also allow further studies on how cell identity is permanently encoded in a cell.