Oxygen deficiency rewires mitochondria
Researchers slow the growth of pancreatic tumour cells
Advertisement
mitochondria burn oxygen and provide energy for the body. Cells lacking oxygen or nutrients have to change their energy supply quickly in order to keep growing. In a study published in Nature, scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing have now shown that mitochondria are reprogrammed under depleted oxygen and nutrients. Tumours of the pancreas may also use this reprogramming mechanism to keep growing despite reduced nutrient and oxygen levels. The researchers believe that proteins in this newly discovered signaling pathway could be a good target for therapies against pancreatic cancer, for which no drug is currently available.
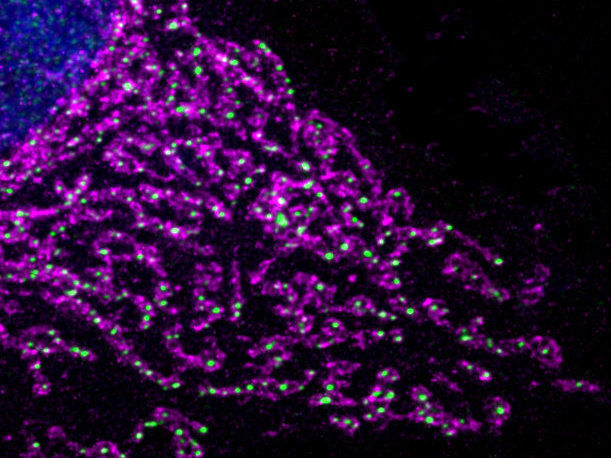
Mitochondria form large networks in the cell. When cells lack oxygen this network is fragmented, mitochondria become fewer and are reprogrammed. (cell nucleus (blue), mitochondria (pink), DNA (green)).
© MPI f. Biologie des Alterns/ Thomas MacVicar
Cells adapt to oxygen deficiency by switching their energy supply to glycolysis, in which sugar is fermented without oxygen. This may be necessary in old age, for example, as the cells in the body are often less supplied with oxygen and nutrients. Also, cancer cells can face this problem, because some tumours have poor blood supply and thus little oxygen and nutrients reach the cells.
"It has been known for some time that cells reduce the number of mitochondria when they lack oxygen and switch to glycolysis. We have now discovered that the remaining mitochondria are additionally reprogrammed to meet the new requirements," explains Max Planck Director Thomas Langer.
Changeover with built-in timer
This happens via a newly discovered signalling pathway in the cell: a protease in the membrane of mitochondria is activated during the conversion to glycolysis and then breaks down various proteins in the organelles. As a result, no new mitochondria can be formed and the remaining mitochondria change their metabolism. This process eventually stops on its own, as the protease begins to degrade itself at high activity. "This signalling pathway not only has a built-in timer, but also enables a very rapid response to oxygen deficiency," said Langer.
Reduced growth of tumour cells
The researchers examined cancer cells originating from patients with pancreatic tumours. These tumours grow under oxygen deficiency and are highly aggressive. The scientists were able to reduce tumour growth by switching off the signalling pathway in the mitochondria. This was seen in cancer cells in the Petri dish as well as in pancreatic tumours in mice. "There is currently no treatment available for pancreatic cancer. I believe that this protease can be a very interesting therapeutic target because we have seen that the signalling pathway is also active in human patients with pancreatic cancer," explains Langer. "However, there are no known substances that have an effect on this protease.”
Original publication
Thomas MacVicar, Yohsuke Ohba, Hendrik Nolte, Fiona Carola Mayer, Takashi Tatsuta, Hans-Georg Sprenger, Barbara Lindner, Yue Zhao, Jiahui Li, Christiane Bruns, Marcus Krüger, Markus Habich, Jan Riemer, Robin Schwarzer, Manolis Pasparakis, Sinika Henschke, Jens C. Brüning, Nicola Zamboni, Thomas Langer; "Lipid signalling drives proteolytic rewiring of mitochondria by YME1L"; Nature; 6. November 2019























































