Detecting bacteria in space
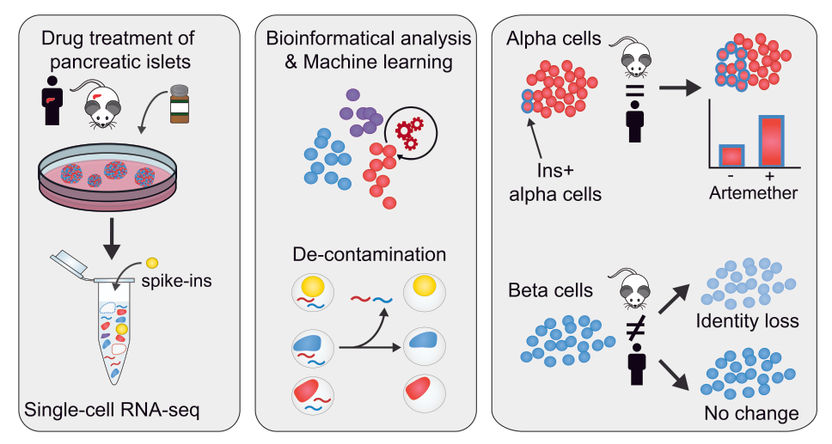
Scientists at Université de Montréal and McGill University have pioneered and tested a new genomic methodology which reveals a complex bacterial ecosystem at work on the International Space Station. Their study is published today in Environmental Microbiology.
Until now, relatively little was known about the different types of microbes found on the space station. The new approach enables researchers to identify and map different species inside the ISS, which will ultimately help safeguard astronauts' health and be key to future long-term space travel. It will also have applications in the realms of environmental management and health care.
"The new methodology provides us spectacular snapshots of the bacterial world in space and the possibilities of applying this method to explore new microbiome environments are really exciting," said Nicholas Brereton, a researcher at UdeM's Institut de recherche en biologie végétale.
The challenge of maintaining cleanliness within space environments was first documented on the Russian MIR space station, where conditions eventually deteriorated so much that mould became widespread. On the ISS, space agencies have been trying to reduce the amount of microbial growth in the station since it was first launched in 1998.
Strict cleaning and decontamination protocols are now in place to maintain a healthy ISS environment; in orbit, crew members regularly clean and vacuum the space station's living and working quarters. But as resupply missions arrive carrying a range of material including food, lab equipment, live plants and animals, new bacteria species are continually being added.
Combined with existing human bacteria, and also because no windows can be opened, the build-up of bacteria inside the cramped quarters can be significant.
"Scientists have a well-documented understanding of broad bacterial families on the ISS, but now we've discovered a more diverse bacterial ecosystem that we ever expected," said Emmanuel Gonzalez, a metagenomic specialist at McGill. "It's an exciting step forward in understanding the biosphere that will accompany humans into extra-terrestrial habitats."
Although the microbial characterization method was piloted in space, its applications will be far broader, say the scientists behind the technology. Researchers can replicate this approach to address many challenges and environments, including in oceans and soils It is already being applied to human diseases and microbiomes.
Most read news
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Acetylcysteine
Theophylline
Hyponastic_response
The_Language_of_the_Genes

How the brain builds panoramic memory - Neuroscientists identify brain regions key to linking different views of our surroundings.