Researchers grow cells in 'paper organs'
Long before scientists test new medicines in animals or people, they study the effects of the substances on cells growing in Petri dishes. However, a 2D layer of cells is a poor substitute for the much more complex 3D structure of tissues in organs. Now, researchers reporting in the ACS journal Nano Letters have used a 3D printer to make paper organs, complete with artificial blood vessels, that they can populate with cells.
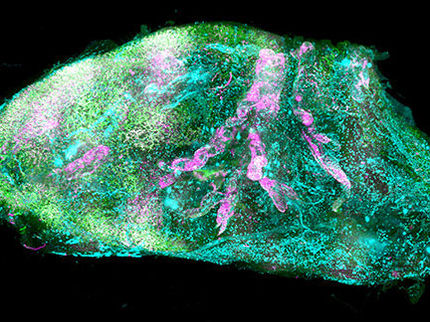
In the body, tissues with similar functions are grouped together in organs, such as the brain, heart or stomach. Organs also contain supporting cells, including nerves, blood vessels and connective tissues. An organ's 3D architecture provides biological, structural and mechanical support to cells that influences how they grow and respond to external stimuli, such as medicines. Yu Shrike Zhang and colleagues wanted to see whether they could combine 3D printing and bacterial cellulose to make supports for artificial organs that they could then fill with cells. Cellulose, a polysaccharide made by plants, algae and some bacteria, is a low-cost material used to make paper.
To create a breast tumor model, the researchers 3D printed petroleum jelly-paraffin ink into a bacterial cellulose hydrogel. Then, they air-dried the hydrogel so that it became porous and paper-like. When they heated the ink, it liquefied and was easy to remove, leaving behind hollow microchannels. The team wet the paper "organ" and added endothelial cells -- the cell type that lines blood vessels -- to the microchannels, and added breast cancer cells to the rest of the structure. Dried paper organs can be stored for long periods of time and then rehydrated to produce inexpensive tissue models, which could be useful for drug screening and personalized medicine, the researchers say.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Speculum_(medical)
Glucosidases
Ankle-foot_orthosis
Severino_Antinori
Category:Relationship_counselling
Sports_injuries
Iron_deficiency_anemia