Imaging nerve-cell interactions
A new imaging technique developed by LMU researchers is garnering lots of attention. Based on a method for making tissues, organs and even whole organisms transparent, it promises to transform studies of the nervous system in particular.
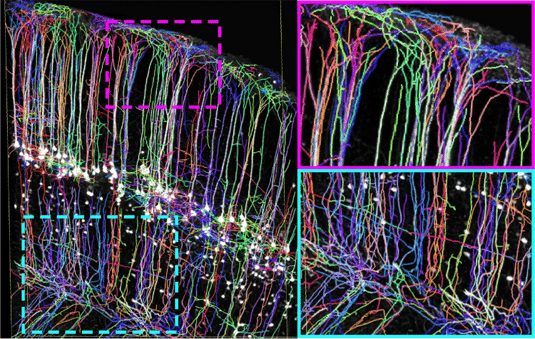
Neuronal structures.
Ertürk Lab
A new bioimaging technology provides unprecedented insights into the interactions of nerve-cell assemblies in mammals and other organisms. The method was developed by Dr. Ali Ertürk, who leads a research group at the Institute for Stroke and Dementia Research at the LMU Medical Center, and the range of its potential applications is so broad that it prompted the appearance of a news article (“‘Invisible’ mice reveal anatomical secrets”) in Nature in November, prior to the publication of Ertürk’s latest findings in the new issue of Nature Neuroscience. The new report describes the technique that is making waves, vDISCO. vDISCO itself represents an extension of a previous method dubbed uDISCO, details of which were first published by Ertürk and colleagues in 2016.
vDISCO renders whole organs and even whole organisms transparent. This in turn makes them accessible to a range of imaging procedures. For instance, researchers can visualize individual cells and ensembles of cells by staining specific proteins with antibodies that have been labelled with fluorescent markers – as the see-through tissue permits passage of the light required to excite the fluorescent signals.
The uDISCO procedure had already permitted Ertürk and his group to obtain detailed views of the intact nervous systems of the mouse. However, clarification of the tissues was incomplete, such that traces of bones and other tissues were still visible. For vDISCO, the mixture of chemicals used to clear tissues has been modified, yielding the first technique that is capable of making whole animals fully transparent.
The new procedure thus allows one to visualize and characterize the full complexity of the nervous systems of small mammals, and will also allow researchers to trace the cellular interactions that lead to inflammation and wound healing, for example. According to the news article in Nature, vDisko has already revealed unexpected structural connections between remote organs – a discovery which, among other things, could lead to new treatments for stroke patients.
Most read news
Original publication
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Age_Standardized_Mortality_Rates
Mitral_regurgitation
Seven_Sleepers
Richard_Anthony_Jefferson
NIST calculations may improve temperature measures for microfluidics
Discrete_nanoscale_transport
Intertek Acquires Divisions of Ciba Expert Services from BASF - Expands Services Globally
Helix BioPharma Corp. Completes Enrollment in Its Phase II Trial of Topical Interferon Alpha-2b
List_of_surgeons