New high-throughput screening study may open up for future Parkinson's disease therapy
Advertisement
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the most common movement disorder in the world. PD patients suffer from shaking, rigidity, slowness of movement and have difficulties walking. It is neurodegenerative disease and is caused by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the brain. Currently PD cannot be cured or even halted in its development, but symptoms may be treated to some degree. Probably the single most important cause of PD is the aggregation of the natively unfolded protein α-synuclein (αSN). αSN can form both small oligomeric complexes (αSOs) as well as large fibrillary deposits; the αSOs are thought to be the most toxic species. If we can prevent or reduce αSN aggregation we have a good way to halt PD development. So far it has been difficult screen large numbers of compounds to identify potential aggregation inhibitors, since αSN aggregates in a rather irregular and variable fashion; it is also difficult to detect early-stage αSOs.
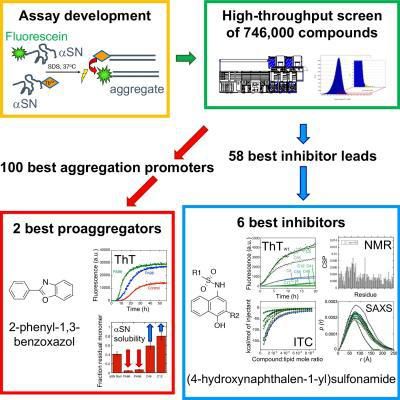
New screening strategy gives rise to identification of novel inhibitors of α-synuclein aggregation, which may help develop a cure for Parkinson's disease. Here is a graphical overview of the screening of 746,000 compounds for the inhibitory effects.
Daniel Otzen
However, in the new screening strategy, the researchers first developed a smart trick to make αSN aggregate in a more predictable way using the "soap" molecule sodium dodecyl sulfate. To detect the aggregates, they then used Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET), a widely used technique for measuring distances within and between molecules. In this way they were able to screen 746,000 compounds for their ability to inhibit αSN aggregation.
By sifting through the results, they came up with a collection of structurally diverse, novel small compounds that either prevent (inhibitor) or accelerate (proaggregator) αSN aggregation. The six best inhibitors share a common core structure and these compounds all interact with the first part of αSN, called the N-terminal region.



























































