Structure of S. agalactiae toxin identified
Streptococcus (S.) agalactiae (contains the CAMP factor) is a round bacterium that could cause severe invasive infections. biologists team led by Prof. JIN Tengchuan from University of Science and Technology of China of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Dr. Eric Brefo-Mensah from the University of Waterloo revealed the structure of S. agalactiae CAMP factor and the mechanism behind for the first time.
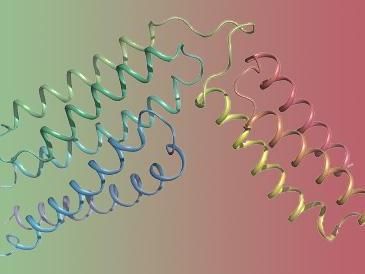
The overall structure of the group B streptococcus CAMP factor.
JIN Tengchuan
By utilizing X-ray diffraction technique, researchers reported the structural fold of S. agalactiae CAMP factor is composed of 5+3 helix bundles, where the N-terminal 5 helix bundle is believed to be responsible for membrane permeabilization and the C-terminal 3 helix bundle is likely responsible for host receptor binding. Besides, the C-terminal domain is revealed to inhibit the activity of both full-length toxin and its N-terminal domain.
The researchers also observed that the linker region has a conserved DLxxxDxAT sequence motif, which is required for CAMP factor's co-hemolytic activity. The results helped clarify the molecular mechanism of S. agalactiae's co-hemolytic activity.
What the researchers illustrated may assist in the screening of anti-CAMP virulent factor drugs and inspire more to reveal the nature of the interaction between proteins and biofilms.
Original publication
Most read news
Original publication
Tengchuan Jin, Eric Brefo-Mensah, Weirong Fan, Weihong Zeng, Yajuan Li, Yuzhu Zhang, and Michael Palmer; "Crystal structure of the Streptococcus agalactiae CAMP factor, and insights into its membrane-permeabilizing activity"; J. Biol. Chem.; 2018
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.