Enigmatic gene critical for a healthy brain
Advertisement
Since the human genome was first sequenced in 2001, scientists have puzzled over swathes of our DNA that despite apparently lacking function are made into ribonucleic acid (RNA) by the cell. Why make RNA at all when it is not then used to make proteins, which perform fundamental biological tasks? Perhaps these so-called non-coding RNAs perform critical, but as yet unknown, tasks?
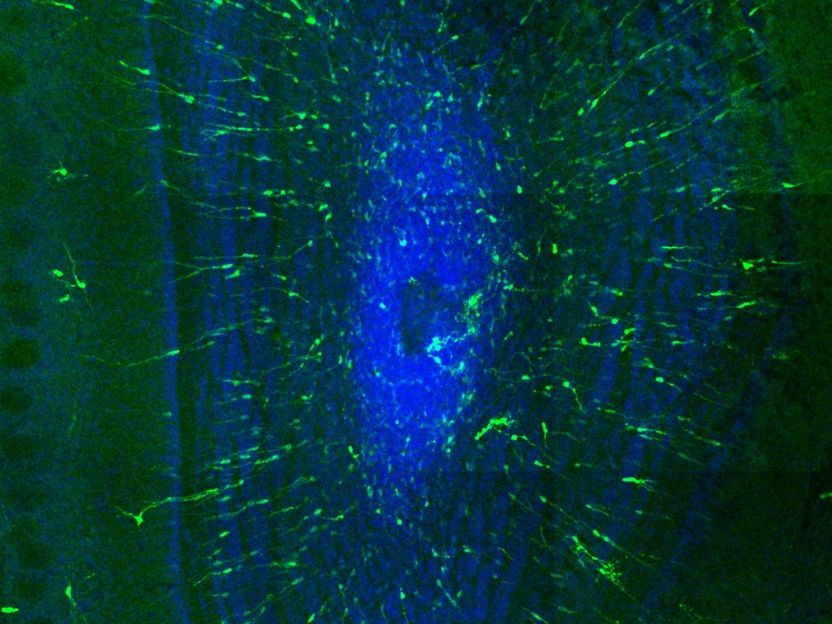
A cross section of the mouse olfactory bulb. Green is electroporated neuroblasts born in the sub ventricular zone that migrated into the olfactory bulb. Blue is a DAPI nuclear counterstain.
Francis Szele
Scientists from the Universities of Bath, Oxford and Edinburgh have now identified one such non-coding RNA, called Paupar, which influences how healthy brains develop during early life. They have shown that Paupar orchestrates proteins that control neurodevelopment.
They studied KAP1, a gene that codes for an essential protein associated with several fundamental processes in neurodevelopment. The KAP1 protein acts as a regulator for several other genes which allow the brain to grow healthily and develop several types of brain cell.
Using molecular biology techniques they discovered that Paupar can act as a switch, modulating how KAP1 acts by binding to it- thus influencing the development of healthy brains in mice. It is the first time that a non-coding RNA has been shown to bind to KAP1.
Dr Keith Vance, from the University of Bath Department of Biology & Biochemistry led the research. He said: "It is now clear that the genome expresses many non-coding RNAs that are not made into protein. Despite this, there is a lot of controversy regarding their function. Some groups argue that these non-coding RNAs are a result of transcriptional noise with no apparent use whilst others think that the vast majority of them must be doing something important.
"We have shown here good evidence that one of these genes, called Paupar, is important for development of the brain.
"It's a young field, but I think it's clear we have to reassess the central dogma of molecular biology that DNA is transcribed to RNA that codes for a protein. We're now seeing that some RNAs can go off and do something themselves.
"Our findings also help us understand the essential role of KAP1, which is something we're really interested in as we look at the development of the central nervous system."



























































