Researchers make a fly’s heartbeat visible
Looking into a tiny fly’s heart: researchers at the Cells-in-Motion Cluster of Excellence at the University of Münster have developed a new method for visualizing the heartbeat of living fruit-fly pupae and automatically recording the pulse frequency. The system has a number of benefits: the images are produced with a camera, without any elaborate microscopy. The technique is non-invasive – in other words, it can all be done on a living creature without any dissection being necessary. The method makes it possible to observe several fly pupae, which are about three millimetres in length, simultaneously.
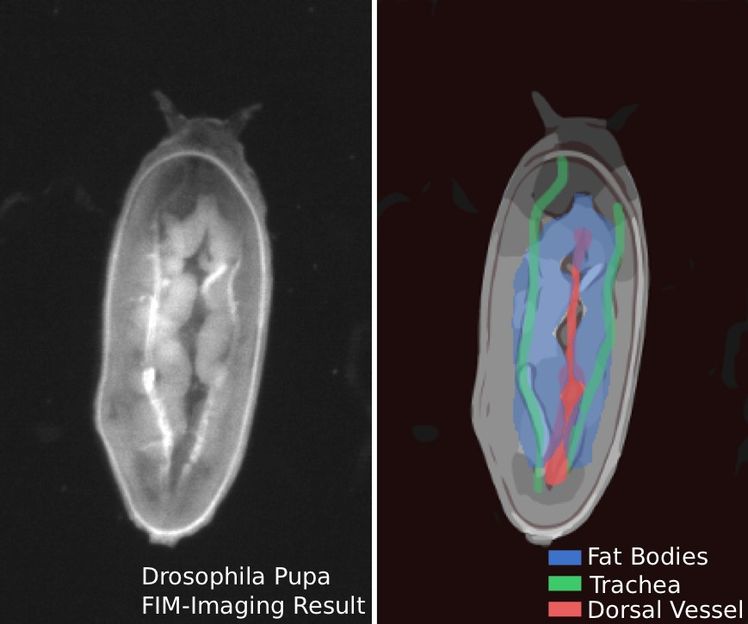
A fruit-fly pupa (the dorsal part of the pupae is facing the camera; the head is up). Right picture: Central organs are labelled
Dimitri Berh, Benjamin Risse
The equipment making it possible to take a look at a fly’s heart is the so-called FIM table. This was developed jointly by researchers from two teams – that led by Prof. Xiaoyi Jiang at Münster University’s Computer Science Department, and the one headed by Prof. Christian Klämbt at the Institute for Neuro- and Behavioural Biology. The table with the Perspex plate actually has a special purpose: to automatically record and evaluate the movements of fly larvae. For biologists, this information on behaviour is important, for example in order to draw conclusions about the functions of genes.
Observing behaviour wasn’t all that was done, however. As fly larvae are translucent, the inner organs can be recognized on the FIM table, at least partially. This is the characteristic on which the current heartbeat study is based – as well as on a stroke of luck. “At some point we had larvae on the table which turned over onto their backs. This enabled us to see that in this position the heart could be recognized using our FIM technology,” recalls computer scientist Dr. Benjamin Risse, now a professor and team leader at the Computer Science Department. He had already designed the observation table – which is now patented – while he was engaged on his doctoral dissertation.
The researchers systematically pursued their work on visualizing the heartbeat – using fly pupae, which are motionless and thus more suitable for studying the pulse. They developed algorithms which automatically recognize and quantify the pulsating movement of a fly’s heart in the video images. For observation purposes the researchers lay the animals belly-up on the FIM table when they are at an early stage of development, as so-called pre-pupae.
The Drosophila melanogaster fruit-fly is an important object of research in biology. Although the fly’s heart is structured very differently than in mammals, there are fundamental aspects in their development and functions which are to similar to those in humans. This means that examining flies can help towards a better understanding of cardiovascular diseases in humans.
For the FIM table, the so-called frustrated total internal reflection (FTIR) of light is used. It is this which gives rise to the project name “FTIR-based imaging method”, or FIM. The method is based on light reflection within the Perspex plate and on the influence on the reflection on the part of the organisms being observed.
Original publication
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.