Breakthrough for peptide medication
The “Holy Grail” of peptide chemistry: Making peptide active agents available orally
peptides, short amino acid chains that control many functions in the human body, represent a billion-dollar market, also in the pharmaceutical industry. But, normally these medications must be injected. A research team led by the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has now determined how peptides can be designed so that they can be easily administered as a liquid or tablet.
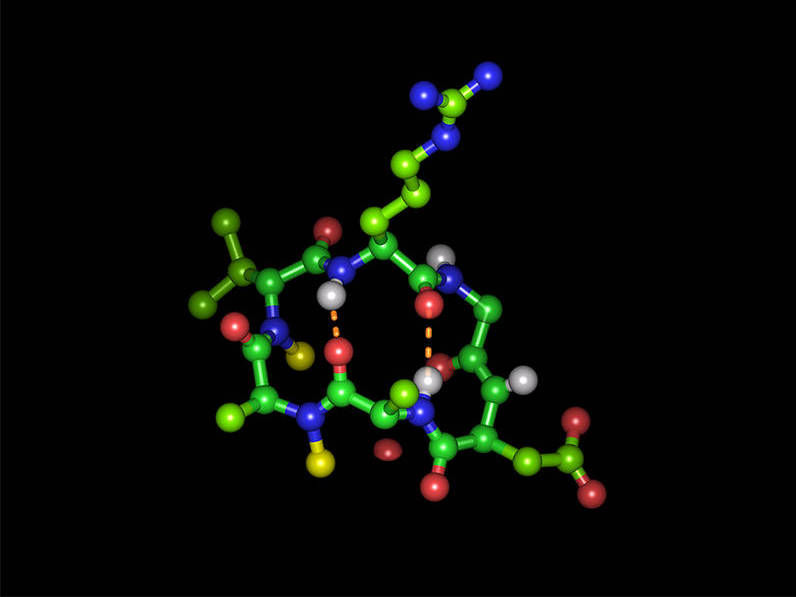
Cyclic hexapeptide in its bioactive form with the integrin-binding tripeptide sequence arginine-glycine-aspartic acid: Green spheres represent carbon atoms, red oxygen atoms, blue nitrogen atoms and white hydrogen atoms. Yellow spheres represent the two N-methyl groups and dashed orange lines show the two intramolecular hydrogen bonds. Arrangement (clockwise): arginine (top), glycine, aspartic acid, alanine, N-methylated alanine, N-methylated D-valine.
Michael Weinmueller / TUM
Peptides are short chains of amino acids. In the human body, they control diverse functions as signaling molecules. Well-known examples include insulin, which comprises 51 amino acid building blocks and controls the metabolism of sugar, or cyclosporine, an eleven amino acid-peptide that has been proven to suppress organ rejection after transplants.
“Peptides are wonderfully well-suited as medication,” says Horst Kessler, Carl von Linde Professor at the Institute for Advanced Study at TU Munich. “The body already uses them as signaling molecules, and when they have done their job, they can be recycled by the body – no accumulation, no complicated detoxification.”
Worldwide, there are currently some 500 peptide-based medications in clinical trials. A handful of peptide medications are already commanding revenues in the billions. But the fact that they cannot be administered as tablets is a decisive disadvantage of almost all substances in this category.
A hurdle race
Since proteins are an important part of the diet, the stomach and intestines harbor countless enzymes that break peptide bonds. No medication based on unmodified peptides would have a chance to survive the passage through the gastrointestinal tract.
Yet even when appropriately modified peptide compounds make it through the stomach intact, another hurdle awaits them: The cells of the intestinal walls prevent their absorption into the blood. That is why these kinds of active agents are generally only be administered by injection.
The path through the wall
The team initially approached these challenges using a ring-shaped model peptide. It comprised six molecules of the simplest amino acid, alanine. The scientists used it to investigate what effect replacing hydrogen atoms of the peptide bonds with methyl groups has on oral availability.
This resulted in over 50 variations. Cellular tests by collaboration partners in Israel showed that only specific peptide variants are absorbed very quickly. “It appears that cyclic hexapeptides with a specific structure are able to use an existing transport system,” says Prof. Kessler.
The biological effect
The team chose integrin receptors that control a variety of functions on the cell surface as a target for their peptides. A sequence of the three amino acids arginine, glycine and aspartic acid is the key to the docking at these receptors. Kessler's co-workers incorporated the key sequence at different positions of their model peptide, thus creating new variants.
However, both the negatively charged side chain of aspartic acid and the positively charged arginine turned out to be knock-out criteria for using the transport system. The team nevertheless managed to mask the charged groups of both amino acids with protecting groups.
Although with this the peptide initially loses its ability to bind to the target molecule, if the right protective groups are selected, they are split off again by enzymes that are ubiquitous in the blood. The pharmaceutical effect is thus restored upon arrival at their destination.
Proof of oral availability
Cell tests have shown that the new hexapeptide indeed has a biological effect. In low doses it stimulates the growth of blood vessels. When mice are fed the masked hexapeptide, the effect is the same as in those that were injected with the unmasked hexapeptide.
“In the past, experts have designated the oral availability of peptide-based medications as the ‘holy grail of peptide chemistry.’ Our work provides a strategy for solving the challenges of stability, absorption in the body and biological effectiveness," says Kessler. "In the future, this will greatly simplify the creation of peptide medication that can be easily given in fluid or tablet form.”
Original publication
"Overcoming the lack of oral availability of cyclic hexapeptides: Design of a selective and orally available ligand for the integrin alphaVbeta3"; Michael Weinmüller et al.; Angewandte Chemie International Edition; 18.12.2017, 56, 16405-16409
"Improving oral bioavailability of cyclic peptides by N-methylation"; Andreas F. B. Räder, Florian Reichart, Michael Weinmüller, Horst Kessler; Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry; 2017, in press
"Exploring the Role of RGD-Recognizing Integrins in Cancer"; Markus Nieberler, Ute Reuning, Florian Reichart, Johannes Notni, Hans-Jürgen Wester, Markus Schwaiger, Michael Weinmüller, Andreas Räder, Katja Steiger and Horst Kessler; Cancers; 2017, 9, 116