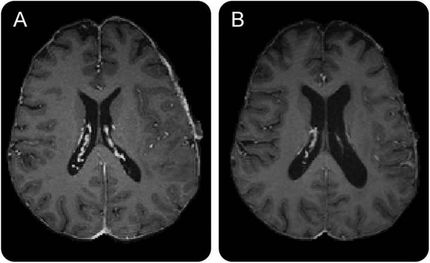
Experimental drug shows promise against brain, prostate cancers
An experimental drug currently being tested against breast and lung cancer shows promise in fighting the brain cancer glioblastoma and prostate cancer, researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center have found in two preclinical studies. The drug's actions, observed in isolated human cells in one trial and in rodents in the other, are especially encouraging because they attacked not only the bulk of the tumor cells but also the rare cancer stem cells that are believed to be responsible for most of a cancer's growth, said Dr. Jerry Shay, professor of cell biology and a senior co-author of both papers. The glioblastoma study appears in the January issue of Clinical Cancer Research . The prostate cancer study is available in the International Journal of Cancer. In the glioblastoma study, performed in mice, the drug also crossed from the bloodstream into the brain, which is especially important because many drugs are not able to cross the blood-brain barrier.
"Because it attacks a mechanism that's active in most cancers, it might prove to be widely useful, especially when combined with other therapies," said Dr. Shay.
Dr. Shay and his colleagues study telomeres, bits of DNA that help control how many times a cell divides. Telomeres are protective "caps" of DNA on the ends of chromosomes, the structures that contain the body's genes. As long as telomeres are longer than a certain minimum length, a cell can keep dividing. But telomeres shorten with each cell division, so a cell stops dividing once the telomeres are whittled down to that minimum. In cancer cells, however, an enzyme called telomerase keeps rebuilding the telomeres, so the cell never receives the cue to stop dividing. In essence, they become immortal, dividing endlessly. The drug used in these studies (imetelstat or GRN163L) blocks telomerase. It is already in clinical trials as a potential treatment for breast and lung cancer, as well as for chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
The researcher focused on cells called tumor-initiating cells. Some researchers believe that tumors contain a small subset of initiating cells – or cancer stem cells – that are able to initiate and drive tumors and that are often resistant to radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
In the glioblastoma study, Dr. Shay and his colleagues found that imetelstat blocked the action of telomerase in isolated tumor-initiating cells as well as the bulk of the tumor cells, eventually killing the cells. Combining imetelstat with radiation and a standard chemotherapy drug made imetelstat even more effective. When the researchers implanted human tumor-initiating cells into rodents, they found that imetelstat was able to enter brain tissue and inhibit telomerase activity.
In the prostate cancer study, the researchers isolated tumor-initiating cells from human prostate cancer cells. The cells showed significant telomerase activity. Imetelstat blocked the enzyme's activity, and telomeres shortened greatly.
Most read news
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents

What can bulls tell us about men? - Towards a better understanding: Which genes and mechanisms control male fertility?
New screening technique paves the way for protein drugs from bacteria
Morning_Glory_syndrome
Researchers develop chemical reaction method for more efficient drug production
Biogen Idec Initiates Phase III Trial of Galiximab for Follicular Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Mystery solved: The health benefits of dark chocolate
Fatty acids from GM oilseed crops could replace fish oil

Gilead Sciences to Acquire MYR GmbH - One of the largest trade sales of a VC-financed German biotech start-up in the last 20 years - first HTGF unicorn
DSM to form global anti-infectives joint venture with Sinochem Group
Actelion and Roche enter into autoimmune disorder collaboration
Canadian authorities grant product approval for Intercell's Vaccine to prevent Japanese Encephalitis