Stroke and heart disease trigger revealed in new research
Advertisement
Scientists have identified the trigger that leads to the arteries becoming damaged in the disease atherosclerosis, which causes heart attacks and strokes, in research published in Circulation. The authors of the study, from Imperial College London, say their findings suggest that the condition could potentially be treated by blocking the molecule that triggers the damage. The research also suggests that bacteria may be playing a part in the disease.
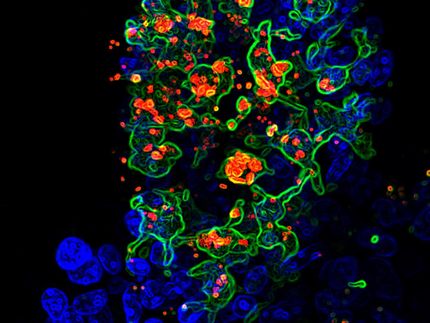
In atherosclerosis, 'plaques' form in arteries that feed the brain and heart, obstructing the blood flow. The plaques are made of substances like fatty deposits and cholesterol. Immune cells are attracted into these plaques, which form inside the wall of the artery, leading to the artery becoming inflamed and to the artery wall being damaged. Sometimes, the plaque can burst as a result of this damage, causing a stroke or a heart attack.
The research, which was funded by the British Heart Foundation and the European Commission, reveals the trigger that leads to the inflammation and damage to the artery wall. The researchers hope they can block this trigger in order to prevent damage to the artery and, ultimately, heart attacks and strokes.
The trigger identified in the research is a molecule called TLR-2. This 'receptor' molecule lives on the surface of an immune cell and when it recognises harmful molecules and cells, including bacteria, it switches the immune cell into attack mode, to protect the body. It can also switch on the immune cells when the body is under stress.
The research shows that TLR-2 is unusually active in plaques in the carotid artery in the neck. In lab tests, the researchers showed that blocking the TLR-2 receptor stopped cells from making the molecules that cause inflammation and damage to the artery. This, they say, suggests that the molecule is triggering the damage to the artery. It also suggests that 'danger molecules,' which kick into action when the body is under stress, and bacteria, may be triggering damage to the arteries by switching on the TLR-2 molecules, increasing the risk of plaques bursting and causing strokes and heart attacks.
If a drug could be developed that would block TLR-2 molecules, the researchers believe this would potentially treat atherosclerosis and prevent damage to the artery. They say this would ultimately reduce people's risk of strokes and heart attacks.
The researchers studied sections of the carotid artery with atherosclerosis, taken from 58 patients after a stroke. They broke down the artery tissue using enzymes, until the researchers had a suspension of single cells in liquid. They analysed the liquid after four days and found that the cells had produced an unusually large amount of inflammatory molecules and enzymes that damage arteries.
The researchers then grew the cells with several different antibodies designed to block different receptors and molecules involved in the inflammation process. The researchers showed that blocking TLR-2 using an antibody reduced the production of inflammation molecules and enzymes dramatically. The team now hopes to pinpoint specific parts of molecules that switch on TLR-2 and trigger inflammation.
Other news from the department science
Most read news
More news from our other portals
See the theme worlds for related content
Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous

Topic world Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized molecules of our immune system that can specifically recognize and neutralize pathogens or foreign substances. Antibody research in biotech and pharma has recognized this natural defense potential and is working intensively to make it therapeutically useful. From monoclonal antibodies used against cancer or autoimmune diseases to antibody-drug conjugates that specifically transport drugs to disease cells - the possibilities are enormous