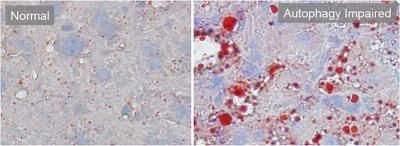
GENFIT: A new potential indication for GFT505, diabetes associated fatty liver diseases
GENFIT revealed complementary beneficial effects of its most advanced proprietary drug candidate GFT505 in prediabetic patients suffering from atherogenic dyslipidemia. In addition to its effects on plasma lipids and specific apolipoproteins, GFT505 significantly improved markers of liver dysfunction in these patients at risk of developing non alcoholic liver disease and steatohepatitis (NAFLD and NASH).
Patients treated with GFT505 demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in plasma triglycerides and an increase in plasma level of “good cholesterol” (HDL-C). Concomitantly, significant reductions vs placebo were observed in apolipoproteins associated with pro-atherosclerotic particles ApoCIII (p=0.04) and ApoB (p=0.02). Furthermore, GFT505 significantly increased plasma levels of ApoA1 (p=0.002) and ApoA2 (p<0.0001), two important constituents of HDL anti-atherosclerotic particles.
Importantly, GFT505 had clear statistically significant beneficial effects on two hallmarks of fatty-liver dysfunction, alanine amino transferase (ALAT: 15% decrease vs placebo, p=0.02) and Gamma glutamyl transpeptidase (gGT: 20% reduction vs placebo, p<0.0001) while it did not affect plasma level of aspartate amino transferase (ASAT). Relative to exisiting lipid lowering drugs, these effects on markers of liver dysfunction are clear assets for the management of overweight prediabetic and diabetic patients, whom the majority is known to have fatty liver disease and is at risk of developing steatohepatitis.
Pr. Bart Staels, President of the Scientific Advisory Board stated: “The GFT505-2083 trial supports GFT505 as an original drug candidate for simultaneously managing multiple co-morbidities related to (pre)diabetes. Furthermore, these latest results clearly offer new perspectives for GFT505 in the prevention/treatment of NAFLD and NASH which merit specific studies through dedicated clinical trials.”
Other news from the department research and development

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Alcohol tolerance 'switch' found - Implications sought in human alcohol consumption, liver disease
Zombie cancer cells eat themselves to live
Biomagnetics (BMGP) Enters Chinese Biotech Market

NasVax Ltd. - Ness-Ziona, Israel

IRsweep AG - Stäfa, Switzerland
Bayer acquires exclusive rights to Bioton’s insulin SciLin