One step closer to an artificial nerve cell
Scientists at the Swedish medical university Karolinska Institutet and Linköping University are well on the way to creating the first artificial nerve cell that can communicate specifically with nerve cells in the body using neurotransmitters. The technology has been published in an article in Nature Materials.
The methods that are currently used to stimulate nerve signals in the nervous system are based on electrical stimulation. Examples of this are cochlear implants, which are surgically inserted into the cochlea in the inner ear, and electrodes that are used directly in the brain. One problem with this method is that all cell types in the vicinity of the electrode are activated, which gives undesired effects.
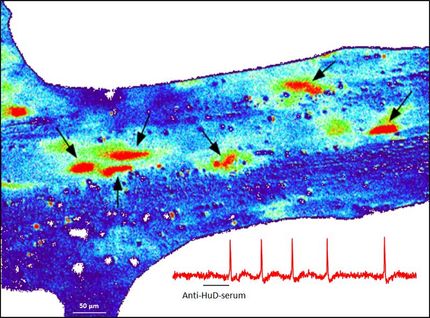
Scientists have now used an electrically conducting plastic to create a new type of “delivery electrode” that instead releases the neurotransmitters that brain cells use to communicate naturally. The advantage of this is that only neighbouring cells that have receptors for the specific neurotransmitter, and that are thus sensitive to this substance, will be activated.
The scientists demonstrate in the article in Nature Materials that the delivery electrode can be used to control the hearing function in the brains of guinea pigs.
“The ability to deliver exact doses of neurotransmitters opens completely new possibilities for correcting the signalling systems that are faulty in a number of neurological disease conditions”, says Professor Agneta Richter-Dahlfors who has led the work, together with Professor Barbara Canlon.
The scientists intend to continue with the development of a small unit that can be implanted into the body. It will be possible to program the unit such that the release of neurotransmitters takes place as often or as seldom as required in order to treat the individual patient. Research projects that are already under way are targeted towards hearing, epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.
The research is being carried out in collaboration between the research groups of Professor Agneta Richter-Dahlfors and Professor Barbara Canlon, together with Professor Magnus Berggren’s group at Linköping University. The work falls under the auspices of the Center of Excellence in Organic Bioelectronics, financed by the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research and led by Magnus Berggren and Agneta Richter-Dahlfors.
Original publication: Daniel T. Simon et al.; “Organic electronics for precise delivery of neurotransmitters to modulate mammalian sensory function”; Nature Materials, Advance Online Publication, 5 June 2009
Most read news
Topics
Organizations
Other news from the department science

Get the life science industry in your inbox
By submitting this form you agree that LUMITOS AG will send you the newsletter(s) selected above by email. Your data will not be passed on to third parties. Your data will be stored and processed in accordance with our data protection regulations. LUMITOS may contact you by email for the purpose of advertising or market and opinion surveys. You can revoke your consent at any time without giving reasons to LUMITOS AG, Ernst-Augustin-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany or by e-mail at revoke@lumitos.com with effect for the future. In addition, each email contains a link to unsubscribe from the corresponding newsletter.
Most read news
More news from our other portals
Last viewed contents
Trinucleotide_repeat_disorders
Hydra can modify its genetic program
Carl_Wedl
Which implementation strategy is right for bio-based chemicals? - Drop-in, smart drop-in and dedicated ones?
Parsing the genome of a deadly brain tumor
Category:EC_3.2.1

Lambda Laboratory Instruments - Zürich, Switzerland